Adding ferrous ions improved the performance of contaminant removal from low C/N coastal wastewater in constructed wetlands†
Abstract
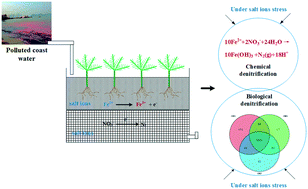
Contaminants in coastal wastewater are prone to induce red tide in sea water and cannot be removed with traditional biological and ecological treatment methods due to salt stress. In this study, constructed wetlands (CWs) were used to remove contaminants from coastal wastewater and the optimal conditions of CWs including C/N ratio and initial contaminant concentration in influents were determined. CW-0.5 (constructed wetlands with a salinity of 0.5‰) was the optimal CW treatment system and realized higher removal efficiencies (75.29% of TN and 76.33% of COD) at 150 mg L−1 COD and 30 mg L−1 in influents after 3 day HRT. After adding 20 mg L−1 ferrous ions, the COD and TN removal efficiencies were respectively increased by 8.67% and 3.71%. According to the high-throughput sequencing results, Thioalkalivibrio was identified to promote denitrification. Under salt stress conditions, ferrous ions optimized the microbial community structure and promoted the enrichment of specific bacteria for wastewater treatments. The optimal CW in this study is a promising process for the efficient nitrogen removal from coastal wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...