Platform selection of engineered nanomaterials for water decontamination applications†
Abstract
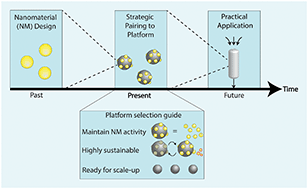
Nano-enabled water treatment processes have become in recent years promising alternatives to conventional water treatment technologies. However, the lack of practical applications of nanomaterials in advancing water treatment systems suggests that major barriers—such as upscaling, practicality, and safety—are hindering their deployment. An effective strategy to overcome barriers associated with nanomaterial implementation in water technologies is their immobilization onto platforms to allow efficient, sustainable, and safe use. Herein, we define the criteria for selection of appropriate platform for decontamination (i.e., removal of chemical contaminants through adsorption or reduction/oxidation), and supply a full critical analysis of top platforms to support engineered nanoadsorbents based on current literature. The criteria for platform selection include strategic material pairing based on contaminant-removal effectiveness of the nanocomposite (i.e., active nanocomponent and platform), sustainable design, and scalability potential. The criteria outlined in this work are generalized and therefore can be used for selection of optimal platform depending on the treatment mechanism (i.e., oxidation, adsorption, etc.). We also highlight the top platforms used in recent literature to support engineered nanoadsorbents and compare the decontaminating performance of the nanocomposite to that of the nanomaterial itself. Further, we pinpoint critical aspects required for sustainable deployment of nano-enabled adsorbing systems such as leaching, regeneration, and reuse. Lastly, we evaluate the maturity and scalability potential of the available platform technologies. Our analysis shows that currently activated carbons are the optimal platform for nanoadsorbents. Overall, this work proposes a powerful tool for platform selection which can be used in future studies and highlight the best-available platform for nanoadsorption technologies – all to ultimately advance safe and effective deployment of nano-enabled water decontamination.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Nanomaterial applications in water and Environmental Science: Nano Cover Art


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...