Joint toxic effects of polystyrene nanoparticles and organochlorine pesticides (chlordane and hexachlorocyclohexane) on Caenorhabditis elegans†
Abstract
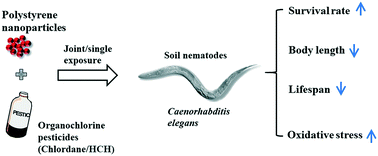
Micro(nano)plastics and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) are common contaminants, however, their joint effects on organisms are largely unknown. In this study, we employed the in vivo system of Caenorhabditis elegans for exposure to 1.0 mg L−1 PS nanoparticles (NPs) and/or two types of OCPs, i.e. chlordane and hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) with a series of concentrations between 0.1 and 10.0 mg L−1. The results showed that a 2 day exposure to both chlordane and HCH induced similar adverse effects including lethality, growth inhibition and lifespan reduction. Compared to single OCPs, their joint exposure with NPs caused stronger chronic toxicity including the reduction of body length and lifespan but weaker acute lethality. The mean lifespans of chlordane- and HCH-joint groups were significantly shortened by 16.2% and 11.8% compared to the single exposure group. Furthermore, joint exposure elevated the expression of glutathione S-transferase-4 (gst-4), a key enzyme in oxidative stress, both in concentration- and time-dependent manners. This reflects that oxidative damage is involved in the mechanisms of joint toxicity. Altogether, this study reveals that nanoparticles can enhance the chronic toxicity of organochlorine pesticides, which suggests the high eco-environmental risk of their co-presence.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...