Selective recovery of Cr from electroplating nanosludge via crystal modification and dilute acid leaching†
Abstract
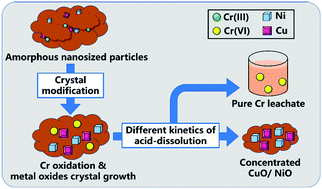
We investigated the selective recovery of Cr from electroplating sludge, which is vital for minimizing environmental pollution and recycling metal resources. In electroplating sludge, Cr, Ni, Cu, and other heavy metals coexist as amorphous nanosized particles, promoting their simultaneous dissolution during traditional concentrated acid leaching and hindering their stepwise recovery. Fortunately, based on their nanosized and amorphous properties, the modification and growth of nanocrystals become practicable, which could cause different solubilities for different metal compound crystals in leaching. Therefore, this study aimed to introduce a calcination and dilute acid leaching method for modifying the crystals/phases of heavy metal compounds and inducing their different acid-dissolution kinetics. The screening revealed NaOH as the optimal additive for recovering 90.2% of Cr from an electroplating sludge with a purity (relative concentration in the leachate) of 96.4%. Investigation of the extraction mechanism demonstrated that calcination of the sludge with NaOH oxidized most Cr(III) compounds to Na2CrO4 and CaCrO4 with high acid solubility. Meanwhile, amorphous Ni and Cu compounds were transformed into NiO and CuO nanocrystals (about 100 nm) with lower kinetics of acid-dissolution. This study indicates the feasibility of “crystal modification” for selective recovery of Cr from electroplating sludge, which overcomes the nonselectivity of the concentrated acid leaching method and highlights a new approach for recovering heavy metals from other nanosludge.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Remediation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...