Sorption of sulfamethoxazole on biochars of varying mineral content
Abstract
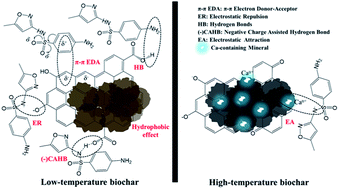
The sorption characteristics of ionizable organic contaminants on biochars are currently unclear, largely because of the different mineral content and pH of the investigated biochars. This study examines the sorption of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) on a number of biochars with different ash contents (KCl and Ca-containing minerals), surface areas (SAs), and acid–basic properties. SMX sorption on biochars produced at 200 °C showed higher sorption compared to sorption on biochars produced above 300 °C due to the hydrophobic effect, hydrogen bonds, and π–π electron donor–acceptor interactions (π–π EDA interactions) resulting from a larger fraction of neutral SMX present in the sorption system. Under alkaline conditions, less sorption nonlinearity was observed, probably resulting from the limited contact between the dissociated SMX− and the negatively charged surface of biochars. Significant sorption observed at alkaline pH was attributed to the negative charge assisted hydrogen-bond (–(CAHB)). When the pyrolysis temperature increased above 400 °C, the increase in the SA of the biochars facilitated apparent sorption. Ca-containing minerals in biochars may provide additional sorption sites for SMX− through electrostatic interactions. This study indicates that the overall sorption of SMX was governed by a combination of factors such as the surface charge, functional groups, SA, and mineral composition of biochars.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...