Synthesis, characterization and anticancer mechanism studies of fluorinated cyclometalated ruthenium(ii) complexes†
Abstract
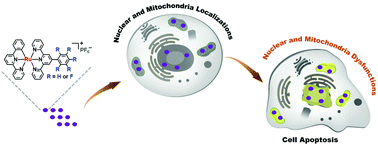
The drug-resistance of cancer cells has become a major obstacle to the development of clinical drugs for chemotherapy. In order to overcome cisplatin-resistance, seven cyclometalated ruthenium(II) complexes were synthesized with a varying degree of fluorine substitution, for use as anticancer agents. A cytotoxicity assay testified that the complexes possessed a more cytotoxic effect than cisplatin towards the cisplatin-resistant cell line A549R. The number of fluorine atoms regulated the lipophilicity of the complexes, but the relationship was not linear. Ru1 containing one fluorine atom had the highest lipophilicity and the best therapeutic effect. The complexes enter cells through an energy-dependent pathway and then localize in the nuclei and mitochondria. The complexes induced nuclear dysfunction by the inhibition of DNA replication as well as mitochondrial dysfunction by the loss of membrane potential. The damage to these vital organelles leads to cell apoptosis via the caspase 3/7 pathway. Our results indicated that the modulation of the number of fluorine atoms in therapeutic agents can have a profound effect and Ru1 is a complex with a high potential as a drug for the treatment of cisplatin-resistant cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...