Spectroscopic characterization of a new Re(i) tricarbonyl complex with a thiosemicarbazone derivative: towards sensing and electrocatalytic applications†
Abstract
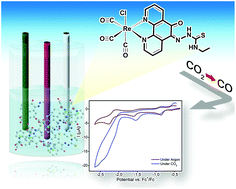
This work describes the preparation of a new thiosemicarbazone derivative, (Z)-N-ethyl-2-(6-oxo-1,10-phenanthrolin-5(6H)-ylidene)hydrazinecarbothioamide (phet) and its respective Re(I) tricarbonyl chloro complex, fac-[ReCl(CO)3(phet)]. The spectroscopic, photophysical and electrochemical properties of the new complex were fully investigated through steady state and time-resolved techniques along with computational calculations. In fac-[ReCl(CO)3(phet)], the new ligand is coordinated to the metal center through the pyridyl rings of the phenanthroline moiety. The unbound electron pairs in the S atom of the bending thiosemicarbazone group induce new low energy lying electronic transitions. Consequently, enhanced visible light absorption up to 550 nm is observed in acetonitrile due to the overlap between MLCTRe→phet and ILphet(n→π*) transitions. The absorption bands and emission quantum yields of fac-[ReCl(CO)3(phet)] are sensitive to proton concentration due to an acid-basic equilibrium in the N atoms of the thiosemicarbazone. Proton dissociation constants of 10.0 ± 0.1 and 11.4 ± 0.2 were determined respectively for the ground and excited states of the new complex. Spectral changes could also be observed in the presence of Zn2+ cations which can be further explored for sensing applications. The electrochemical behavior of the new complex was studied in detail, revealing up to four one electron reduction processes in the range from 0 to −2.4 V vs. Fc+/Fc. With support of DFT calculations, the first three processes are ascribed to the reduction of the coordinated phet ligand followed by the ReI/0 reduction and consequent Cl− release. The new complex was able to act as an electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction into CO (Eonset = −1.92 V vs. Fc+/Fc), with a turnover frequency of 2.81 s−1 and turnover number of 24 ± 1 in anhydrous acetonitrile, being the first Re(I) tricarbonyl complex with a thiosemicarbazone derivative described for this goal. The detailed characterization carried out here can drive the development of new Re(I)-thiosemicarbazone derivatives for different applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Americas


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
