Tuning the oxygen release properties of CeO2-based catalysts by metal–support interactions for improved gasoline soot combustion†
Abstract
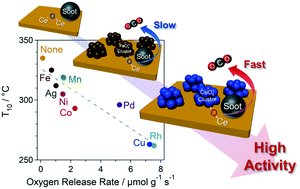
To develop highly active soot combustion catalysts for gasoline direct injection exhausts under low oxygen concentration conditions, CeO2 supported-metal catalysts (M/CeO2, M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Rh, Pd, and Ag) were examined. Among the catalysts tested, Cu/CeO2 and Rh/CeO2 displayed the highest soot combustion activity. By comparing the activities of Cu-based catalysts with and without a Cu–CeO2 interface, the importance of such an interface for soot combustion was inferred. The oxygen release rate of CeO2-based catalysts, enhanced by metal–CeO2 interactions, was indicated as the controlling factor of catalytic activity. The soot oxidation activity and oxygen release rate were also demonstrated to correlate with metal–oxygen bond energy. Based on the redox properties and structural characteristics of CeO2-based catalysts, loading CeO2 with Cu or Rh, which have moderate M–O bond energy, was concluded to be optimal both in terms of the dispersion of supported-metal species and reducibility of the CeO2-based catalyst.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...