An in situ exchange mechanism for dye molecules and cations at the nano-semiconductor film/electrolyte interface†
Abstract
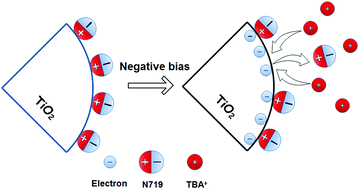
This communication uses electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) in combination with the potentiostatic method to study the in situ exchange mechanism for dye molecules and cations on the nano-film surface under a constant potential. The relationship between dye molecule desorption mass and charge was analyzed. A theoretical model was established to obtain the important parameters of cation exchange number and apparent valence electron number during dye desorption, and the microscopic desorption mechanism of the dye is further revealed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...