Diversified AIE and mechanochromic luminescence based on carbazole derivative decorated dicyanovinyl groups: effects of substitution sites and molecular packing†
Abstract
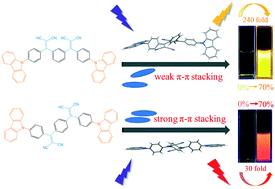
Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties have been widely investigated not only because they thoroughly circumvent the notorious aggregation-caused quenching effect encountered in conventional fluorophores but also due to their promising applications in organic light-emitting diodes, fluorescent sensors and bioimaging. In this work, we reported a study of the molecular packing and luminescence properties of AIE active positional isomers (m-BPCDM and p-BPCDM) with carbazole and dicyanovinyl groups. The compound m-BPCDM based on meta-substitution showed more evident AIE processes than the compound p-BPCDM based on para-substitution, which can be attributed to the strong π–π stacking effect brought by the spatial structure of p-BPCDM. Moreover, the two positional isomers also exhibited distinct mechanochromic luminescence properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...