A heterogeneous bio-inspired peroxide shunt for catalytic oxidation of organic molecules†
Abstract
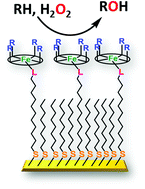
Heme enzymes are capable of catalytically oxidising organic substrates using peroxide via the formation of a high-valent intermediate. Iron porphyrins with three different axial ligands are created on self-assembled monolayer-modified gold electrodes, which can oxidize C–H bonds and epoxidize alkenes efficiently. The kinetic isotope effects suggest that the hydrogen atom transfer reaction by a highly reactive oxidant is likely to be the rate-determining step. Effect of different axial ligands and different secondary structures of the iron porphyrin confirms that the thiolate axial ligand with a hydrophobic distal pocket is the most efficient for this oxidation chemistry.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bioinspired metal complexes for chemical transformations and catalysis


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...