Poly(ionic liquid)-based polymer composites as high-performance solid-state electrolytes: benefiting from nanophase separation and alternating polymer architecture†
Abstract
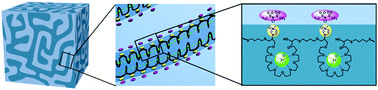
An alternating copolymer-based poly(ionic liquid) (PIL) was synthesized and blended with PVDF-HFP to obtain solid-state polymer electrolytes with both high mechanical strength and high ionic conductivity. Structural analysis reveals that the high performance is attributed to the nanophase separation of PVDF-HFP with a PIL in the nanometric scale, which benefits from an alternating polymer architecture of the PIL.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...