Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Nanoparticle size and chemical modification play a crucial role in the interaction of nano gold with the brain: extent of accumulation and toxicity
Nouf N.
Mahmoud
*a,
Abdulrahim
Albasha
a,
Suhair
Hikmat
a,
Lama
Hamadneh
a,
Rand
Zaza
b,
Ziad
Shraideh
c and
Enam A.
Khalil
d
aFaculty of Pharmacy, Al-Zaytoonah University of Jordan, Amman 11733, Jordan. E-mail: nouf.mahmoud@zuj.edu.jo
bCell Therapy Center, The University of Jordan, Amman 11942, Jordan
cDepartment of Biological Sciences, School of Science, The University of Jordan, Amman 11942, Jordan
dSchool of Pharmacy, The University of Jordan, Amman 11942, Jordan
First published on 16th March 2020
Abstract
Correction for ‘Nanoparticle size and chemical modification play a crucial role in the interaction of nano gold with the brain: extent of accumulation and toxicity’ by Nouf N. Mahmoud et al., Biomater. Sci., 2020, DOI: 10.1039/c9bm02072a.
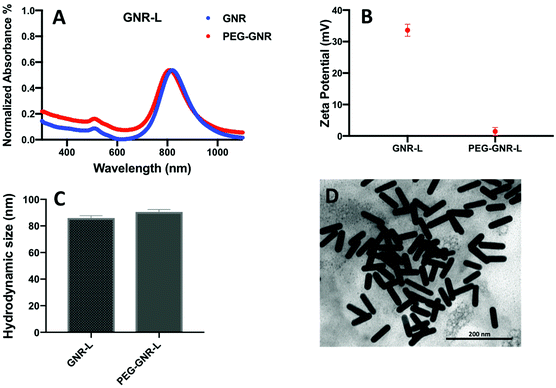
After publication, the authors found an error in Fig. 3D in the main paper. The corrected version of Fig. 3 is shown below.
The authors note that this correction has no effect on the results reported, nor does this change alter any of the contents and conclusions of the paper. The authors sincerely apologize for these inadvertent errors.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |