Increased cross-linking micelle retention in the brain of Alzheimer's disease mice by elevated asparagine endopeptidase protease responsive aggregation†
Abstract
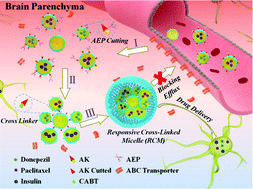
Current forms of medication for Alzheimer's disease (AD) provide a symptomatic benefit limited to those with early onset, but there is no single drug available for later stage patients. Given the recent failures of AD drugs in clinical trials, an intensive treatment strategy based on drug combination that is approved is attractive. At present, the greatest difficulty lies in the low accumulation of drugs in the brain. All hydrophilic drugs are limited by the physical and biochemical barriers within the blood–brain barrier and lipophilic drugs are often transported back into the blood by efflux pumps located in the blood–brain barrier. Here, we select elevated asparagine endopeptidase (AEP) as a target to trigger in situ cross-linking of small sized particles to form large sized drug clusters to block the efflux of the brain. Subsequently, responsive cross-linking micelles (RCMs) loaded with the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, donepezil (DON), the microtubule therapeutic agent, Paclitaxel (PTX), and the glucose metabolism disorder regulator, insulin (INS) are investigated, with a focus on high levels of drug accumulation in the brain in AD. These smart multi-drug delivery RCMs provide a powerful system for AD treatment and can be adapted for other central nervous system (CNS) disorders.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...