A highly selective iron oxide-based imaging nanoparticle for long-term monitoring of drug-induced tumor cell apoptosis†
Abstract
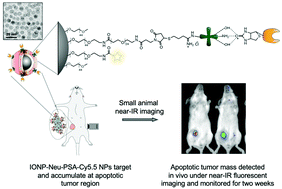
The ability to visualize and quantify apoptosis in vivo is critical to monitoring the disease response to treatment and providing prognostic information. However, the application of current apoptosis labeling probes faces significant challenges including nonspecific tissue uptake, inefficient apoptotic cell labeling and short monitoring windows. Here we report a highly specific apoptosis labeling nanoparticle (NP) probe with Pisum sativum agglutinin (PSA) as a tumor targeting ligand for prolonged in vivo apoptosis imaging. The NP (namely, IONP-Neu-PSA) consists of a magnetic iron oxide core (IONP) conjugated with PSA, and a reporter fluorophore. IONP-Neu-PSA demonstrated minimal cytotoxicity and high labeling specificity towards apoptotic cells in vitro. When applied in vivo, IONP-Neu-PSA tracks apoptotic tumors for a prolonged period of two weeks under near-IR imaging with low background noise. Moreover, IONP-Neu-PSA possesses T2 contrast enhancing properties that can potentially enable apoptosis detection by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The high specificity for apoptotic cells, sustained fluorescence signals, and non-invasive imaging capability exhibited by IONP-Neu-PSA make it a versatile tool for cancer treatment monitoring and pathological research.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biomaterials for Imaging and Sensing


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
