A high flexibility all-solid contact sulfide selective electrode using a graphene transducer†
Abstract
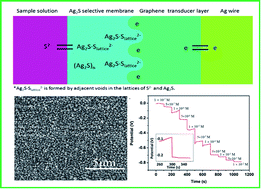
In this paper, a novel high flexibility all-solid contact ion selective electrode (ASC-ISE) based on reduced graphene sheets (RGSs) as the ion-to-electron transducer was developed for rapid detection of sulfide. A graphene layer was firstly electrodeposited on a flexible silver wire by direct reduction of graphene oxide, and nanostructured Ag2S was then prepared as the selective membrane by electrodeposition. Scanning electrochemical microscopy was performed for the characterization of the morphological properties of the RGSs and Ag2S membranes. The evaluation of the analytical performances, such as the linear range, selectivity, stability, and practical application, of the proposed ASC-ISEs for the rapid detection of sulfide was performed. The results showed that, the ASC-ISEs exhibited a linear relationship between the obtained potential signal and sulfide concentration in the range of 0.50 μM to 1.0 mM, with a detection limit of 0.18 μM. Moreover, the ASC-ISEs showed good selectivity towards sulfide over other common interfering ions, and maintained a stable electrochemical response over 7 days. These results demonstrated that graphene was a promising material as the ion-to-electron transducer layer in the development of ASC-ISEs for sulfide detection, and the results of practical applications in tap water and seawater samples showed that the ASC-ISEs held significant promise in a broad range of applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...