A high-throughput plasmonic tongue using an aggregation assay and nonspecific interactions: classification of taste profiles in maple syrup†
Abstract
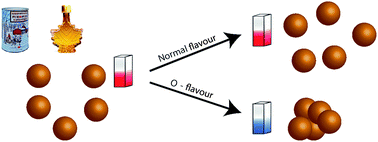
A simple colorimetric test detects off-flavour profiles of maple syrups in minutes, which are detectable by the naked eye. As flavour profiles are due to complex mixtures of molecules, the test uses nonspecific interactions for analysing the aggregation and color change of Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) induced by the different organic molecules contained in off-flavour maple syrup. The test was optimal with 13 nm citrate-capped AuNPs reacting 1 : 1 with pure maple syrup diluted 10 times. Under these conditions, normal flavour maple syrups did not react and the solution remained red, while off-flavoured maple syrups aggregated the AuNPs and the solution turned blue. Different classes of molecules were then tested to evaluate the types of compounds typically found in maple syrups reacting in the test, showing that sulfur- and amine-containing amino acids and aromatic amines caused aggregation of the AuNPs. The test was validated with 1818 maple syrup samples from the 2018 harvest in Quebec and 98% of the off-flavoured maple syrups were positively identified against the standard taste test. Preliminary tests were performed on site in maple sugar shacks to validate the applicability of the test on the production site.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bioanalytical sensors for real world applications


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...