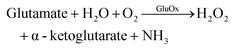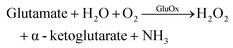Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Glutamate sensing in biofluids: recent advances and research challenges of electrochemical sensors
Jessica
Schultz
a,
Zakir
Uddin
b,
Gurmit
Singh
c and
Matiar M. R.
Howlader
*a
aDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, ON L8S 4K1, Canada. E-mail: mrhowlader@ece.mcmaster.ca
bSchool of Rehabilitation Science, McMaster University, 1400 Main St W, Hamilton, ON L8S 1C7, Canada
cDepartment of Pathology and Molecular Medicine, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, ON L8S 4 K1, Canada
First published on 20th May 2020
Abstract
Correction for ‘Glutamate sensing in biofluids: recent advances and research challenges of electrochemical sensors’ by Jessica Schultz et al., Analyst, 2020, 145, 321–347. DOI: 10.10.1039/C9AN01609K
The authors regret that several sections of the text are incorrect and require adjustments. These are detailed below. In addition, there are errors in Fig. 9, Table 3 and eqn (5).
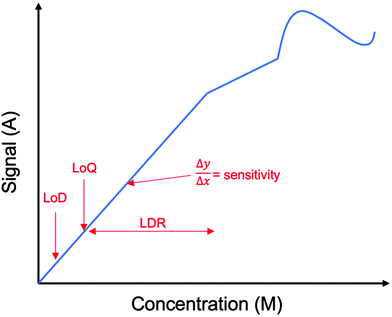
The authors regret that Fig. 9 incorrectly gives the sensitivity as dx/dy. The correct version of Fig. 9 and its caption is presented here.
The authors regret that in Table 3 the 4th generation reactions are incorrect. The correct version of Table 3 is shown here.
The authors regret that eqn (5) was incorrect. The correct version of eqn (5) is given below. Eqn (6) has been added to clarify the dependencies of these processes on glutamate.
| Ni(OH)2 + OH− ↔ NiO(OH) + H2O + e− | (5) |
| NiOOH + glutamate → oxoglutarate + Ni(OH)2 | (6) |
The authors regret that incorrect details were given for ref. 205 in the original article. The correct version of the reference is given below as ref. 1.
The following sentences in the Introduction require adjustment. The sentence beginning “Typically, electrochemical sensors consist of…” should be correctly given as “Typically, electrochemical glutamate sensors consist of a three-electrode system: working, reference and counter electrodes”. The sentence beginning “During cyclic voltammetry, the sensor fabricated…” should be correctly given as “During cyclic voltammetry the sensor, fabricated with a NiO and glassy carbon electrode (GCE), required an OH− during the oxidation of Ni, thus the solution requires high alkaline conditions”.
The following sentences in section 2.1 should be corrected as follows: The sentence on page 322 beginning “Intracellular glutamate is generally inert…” should be correctly given as “While the binding of glutamate to transporters can trigger the propagation of intracellular signals, glutamate can also undergo glutamate uptake or diffusion”. The sentence on page 322 beginning “Similarly, simple diffusion is another mode of…” should be correctly given as “Similarly, simple diffusion is another mode of removal of glutamate”. The sentence on page 323 beginning “Ionotropic glutamate receptors are on…” should be correctly given as “Ionotropic glutamate receptors are on the postsynaptic membrane and include N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) and kainate receptors.40”
The sentence on page 325 beginning “This was determined through completing PCR…” should be correctly given as “This was determined through completing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on the isolated mRNA from each section”.
The following sentences in section 3.2 should be corrected as follows: The sentence on page 325 beginning “Glutamate concentrations are higher…” should be correctly given as “Glutamate concentrations are higher in the plasma at 5–100 μM and in whole blood at 150–300 μM in comparison to in the CSF”. The sentence on page 326 beginning “W. Bai et al. reported elevated blood glutamate levels…” should be removed and the following sentence correctly given as “W. Bai et al. found blood glutamate concentrations increased…”.
The sentence on page 328 beginning “Glutamate and glutamine were measured…” should be correctly given as “Glutamate and glutamine were measured in patients using isotope dilution GC-MS”.
The sentence on page 329 beginning “Biosensors are the biological manipulation of…” should be correctly given as “Biosensors are the biological manipulation of sensors, where an analyte is detected on a bioreceptor or biological recognition element”.
The following sentences in section 5.1 on page 330 should be corrected as follows: The sentence beginning “Potentiometric sensors can be fabricated…” should be correctly given as “Voltammetric or amperometric sensors can be fabricated with two or three-electrode systems”. The sentence beginning “Biosensors have advanced tremendously”. should be correctly given as “Biosensors have advanced tremendously in the past decades since the initial “true” biosensor was brought to life by Leland C. Clark.134” The sentence beginning “When the analyte is detected…” should be correctly given as “When the analyte is detected at the surface of the working electrode, a reduction–oxidation (redox) reaction occurs. This indirectly produces an electron through the production of hydrogen peroxide, and hence produces a current proportional to the concentration of glutamate”.
The following sentences on page 333 should be corrected as follows: In section 5.2.1, the sentence beginning “A lower numerical value…” should be correctly given as “A higher numerical value results in a higher sensitivity, ideal for glutamate detection in healthcare applications. “In section 5.2.2, the sentences beginning “The limit of detection (LoD)…” should be correctly given as “The limit of detection (LoD) is the minimum concentration of glutamate that can be measured with reasonable certainty. According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Goldbook the LoD is calculated with the following equation: where μblank is the mean of blank measures and σblank is the standard deviation of blank measures and k is the numerical factor based on the sought-after confidence level”. In section 5.2.5, the sentence beginning “The limit of quantification…” should be correctly given as “The limit of quantification (LoQ) is higher than the LoD and is the minimum concentration of glutamate quantified to a desired level of precision.148 It can be the lower bound of the LDR, or the lowest concentration of glutamate detected in a linear response”. In section 5.3, the sentence beginning “Inkjet printers are a series of…” should be correctly given as “Inkjet printers produce a series of continuous droplets onto a material”.
The following sentences in section 5.4.1 on pages 334 and 336 should be corrected as follows: The sentence beginning “Electrodes can be fabricated from…” should be correctly given as “Electrodes can be fabricated from a multitude of materials, commonly consisting of platinum (Pt), carbon, or gold (Au)”. The sentence beginning “Analogous to chitosan, polypyrrole…” should be correctly given as “Polypyrrole (PPy) is a conducting polymer used for its ability to reject interference molecules”. The sentence beginning “Variations of phenylenediamine specifically,…” should be correctly given as “Variations of phenylenediamine specifically, meta-phenylenediamine (mPD), ortho-phenylenediamine (oPD) to form poly(o-phenylenediamine) (PoPD) are commonly present among biosensors. Where mPD and oPD are isomers of phenylenediamine and oPD is the monomer used to synthesize PoPD.181,182”
The following sentences in section 5.4.2 on page 338 should be corrected as follows: The sentence beginning “The sensitivity was the second highest…” should be correctly given as “The sensitivity was the second lowest in Table 4 at 395 pA μM−1”. The sentence beginning “Wei et al.'s in vivo sensor…” should be correctly given as “Wei et al.'s in vivo sensor had the lowest sensitivity of 56 pA μM−1”. The sentence beginning “Consequently, the sensitivity improved in…” should be correctly given as “Consequently, the sensitivity improved in PBS, which mimics physiological conditions”.
The sentences in section 5.5.2, on page 339, beginning “The sensor fabricated with a…” should be correctly given as “The sensor fabricated with a NiO electrode demonstrated a poorer sensitivity of 11 μA μM−1 cm−1. However, the sensor with Co3O4 had a sensitivity of 9.5 × 10−5 μM, exhibiting the lowest sensitivity”.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
References
- H. M. N. Ahmad, B. Si, G. Dutta, J. R. Csoros, W. R. Seitz and E. Song, Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Detection Of Glutamate Using Templated Polymer-Based Target Receptors, 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII (TRANSDUCERS & EUROSENSORS XXXIII), Berlin, Germany, 2019, pp. 613–616 Search PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |