Surface-enhanced electrochemiluminescence combined with resonance energy transfer for sensitive carcinoembryonic antigen detection in exhaled breath condensates†
Abstract
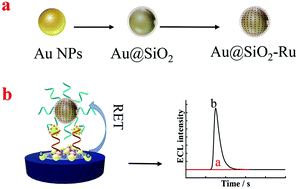
The detection of biomarkers in exhaled breath condensates (EBCs) is regarded as a promising non-invasive diagnostic approach. However, the ultralow concentration of biomarkers in EBCs is a great challenge. Herein, a sensitive dual signal amplification strategy was developed based on surface-enhanced electrochemiluminescence (SEECL) combined with resonance energy transfer (RET). Gold nanoparticles-functionalized graphite-like carbon nitride nanohybrids (Au-g-C3N4 NHs) could be used as an energy transfer donor because of the good overlap between its emission peak and the absorption peak of tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium dichloride (Ru(bpy)3Cl2) at 460 nm. Gold-silicon dioxide core–shell nanoparticles doped with Ru(bpy)32+(Au@SiO2-Ru) were employed as an energy transfer acceptor emitting at 620 nm. Moreover, the signals at 620 nm emitted by Ru (bpy)32+ were enhanced by 5 times, attributed to the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs). The detection of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) was performed by using two aptamers as the recognition unit; whereby aptamer 1 (Apt1) was modified on the surface of Au-g-C3N4 NHs, and aptamer 2 (Apt2) was banded on the surface of Au@SiO2-Ru. In the presence of CEA, a sandwich structure was formed between Au-g-C3N4 NHs-Apt1-CEA and Apt2-Au@SiO2-Ru, which resulted in an ultrasensitive detection of CEA. The proposed electrochemiluminescence sensor showed a wide linear relationship with the CEA concentration in the range from 1.0 pg mL−1 to 5.0 ng mL−1, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.3 pg mL−1. Finally, the practicality of the proposed sensor was demonstrated to detect CEA in EBCs, and the obtained results were in good agreement with the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...