Simultaneous quantification of peroxidase and ascorbic acid in biosamples with an automatic system based on a Fe(iii)/methylthymol blue-carbon dot simulative enzyme†
Abstract
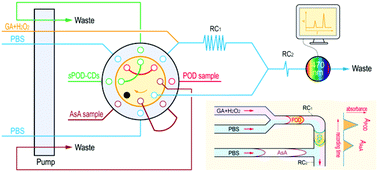
Peroxidase (POD) and ascorbic acid (AsA) usually coexist in organisms to synergistically protect them from reactive oxygen damage, and their contents undergo dynamic changes under different physiological conditions. What's more, the response of POD-catalytic activity in spectrophotometry has to be corrected using the content of concomitant AsA because we found that there is an extinction reaction between AsA and chromogenic products obtained from POD catalysis. With these implications, by skilfully using the chromogenic and the extinction phenomena in the guaiacol/POD/H2O2 reaction, an automatic analysis system for simultaneous quantification of POD (73–440 U L−1) and AsA (4–60 mg L−1) was successfully established based on flow injection analysis (FIA). Furthermore, under acidic conditions (0.5 mol L−1 of HCl), hydrothermal synthesis (250 °C for 1 h) was used for synthesizing new carbon dots (sPOD-CDs) of methylthymol blue (0.08 g L−1)/FeCl3 (0.8 g L−1), which is a simulative enzyme for POD, and it was first used for catalyzing the guaiacol/H2O2 reaction within the FIA system to replace natural HRP in the extinction reaction. This sPOD-CD solution has no background absorption and its concentration shows excellent correlation with simulative POD-activity. Finally, after optimization, this FIA system was utilized to testify that the reducibility of AsA is due to ascorbate ions and to determine POD and AsA in some plant samples. The standard addition recovery experiment showed that there was no interference from the matrix in real samples (recoveries: 95%–105%), and the obtained POD and AsA results were also consistent with the reference experiments (relative deviation ≤ 2.80%, t-test ≥ 0.07). The proposed FIA system is characterized by high sample-throughput (40 samples per h), better repeatability (relative standard deviation ≤ 1.4%), etc.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...