Excellent comprehensive energy storage properties of novel lead-free NaNbO3-based ceramics for dielectric capacitor applications
Abstract
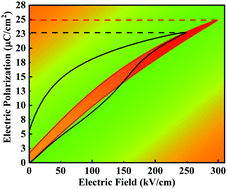
NaNbO3 (NN) is generally considered as one of the most promising lead-free antiferroelectric (AFE) perovskite materials with the advantages of low cost, low density and nontoxicity. However, the metastable ferroelectric phase causes a large remanent polarization (Pr) at room temperature, seriously hindering the achievement of excellent energy storage properties. Although via the strategy of lowering the radius of B-site ions and polarizability, a number of AFE NaNbO3-based solid solutions with double polarization–electric field loops are successfully constructed, the hysteresis losses are still too large and the Pr value cannot be reduced to near zero. In this study, Bi(Mg2/3Nb1/3)NbO3 (BMN) was chosen to partially substitute the pure NaNbO3 with the intention of enhancing antiferroelectricity and constructing a local random field simultaneously. These short-range interactions effectively suppress the hysteresis loss and Pr, and slim hysteresis loops were observed in the NN–BMN ceramics. A high charged energy density (3.4 J cm−3) and recoverable energy storage density (2.8 J cm−3) with high efficiency (82%) were achieved under 300 kV cm−1 for NN–0.10BMN. Superior stabilities and underdamped discharge abilities were also achieved for NN–0.15BMN with a slightly smaller recoverable energy storage density (2.4 J cm−3) but even higher efficiency (90%). The results reported here demonstrate great potential of the designed NN–BMN ceramics for high-temperature capacitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...