A dual-inhibitor system for the effective antifibrillation of Aβ40 peptides by biodegradable EGCG–Fe(iii)/PVP nanoparticles†
Abstract
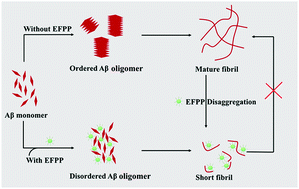
Recently, due to their properties of high surface-to-volume ratio, easy penetration of the blood–brain barrier and easily modified surfaces, nanoparticles (NPs) have been recognized as promising inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease (AD) diagnosis and therapy. However, to achieve clinical application, the design and synthesis of specific NPs with good biocompatibility and degradability still are the main focus of research. In this paper, EGCG–Fe(III)/PVP (EFPP) NPs with ultra-small size and good biocompatibility were first fabricated by the coordination reaction between Fe3+, EGCG and PVP. The obtained EFPP NPs exhibited effective influence on the inhibition of Aβ40 fibrillation and disaggregation of existing Aβ40 fibrils. The inhibitory effect was mainly derived from the synergistic effect of the weak hydrophobicity from PVP and antioxidant activity of EGCG. With the advantages of easy synthesis, high stability in simulated body fluid, high performance towards the antifibrillation of Aβ40 and biodegradability, it is reasonable to consider that the as-prepared EFPP NPs have good application prospects in the treatment of AD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...