Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Effects of LiBOB on salt solubility and BiF3 electrode electrochemical properties in fluoride shuttle batteries
Asuman
Celik Kucuk
 *a,
Taketoshi
Minato
*a,
Taketoshi
Minato
 a,
Toshiro
Yamanaka
a,
Toshiro
Yamanaka
 a and
Takeshi
Abe
*b
a and
Takeshi
Abe
*b
aOffice of Society-Academia Collaboration for Innovation, Kyoto University, Katsura, Nishikyo, Kyoto 615-8530, Japan. E-mail: celikkucuk.asuman.3a@kyoto-u.ac.jp
bGraduate School of Global Environmental Studies, Kyoto University, Katsura, Nishikyo, Kyoto 615-8510, Japan
First published on 21st May 2019
Abstract
Correction for ‘Effects of LiBOB on salt solubility and BiF3 electrode electrochemical properties in fluoride shuttle batteries’ by Asuman Celik Kucuk et al., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 8559–8567.
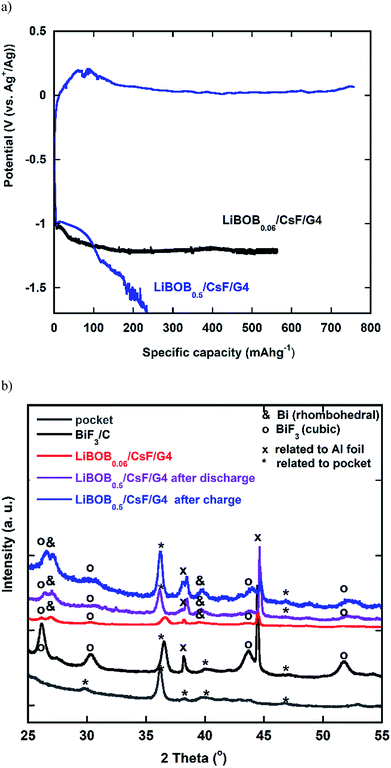
The authors regret errors in the legends of Fig. 5 and 7 in the published article (in which the BiF3 phase was incorrectly labelled as orthorhombic and hexagonal). In addition, on pages 8564 and 8565 of the published article, the phrase ‘orthorhombic BiF3’ should instead have read ‘cubic BiF3’, and on page 8565 of the published article, the phrase 'hexagonal phase' should instead have read 'cubic phase'. Corrected versions of Fig. 5 and 7 are provided below.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |