Degradation and regeneration mechanisms of NiO protective layers deposited by ALD on photoanodes†
Abstract
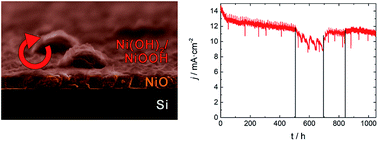
The use of high pH electrolytes requires protective layers to avoid corrosion in photoanodes based on semiconductors like silicon. NiO is one of the materials that comply with the requirements for transparency, conductivity, chemical stability and catalysis on the surface in contact with the electrolyte. Here, NiO layers have been deposited by atomic layer deposition (ALD) at low temperatures, and their stability is analyzed over 1000 hours. Due to the layer structure characteristics, the best overall performance was achieved at 100 °C deposition temperature. By electrochemical measurements progressive time dependent degradation under anodic working conditions is observed, attributed to the formation of higher nickel oxidation states at the electrode/electrolyte interface as a main degradation mechanism, resulting in an OER overpotential increase. Another minor degradation mechanism affects the optical surface quality and gives rise to a loss of photon absorption efficiency on the scale of hundreds of hours. A regeneration process based on in situ periodic cyclic voltammetry, bringing the electrodes to cathodic conditions every 3, 12 or 48 hours, has been shown to partially reverse the main degradation mechanism achieving 85% stability over 1000 hours in a study with over 10 mA cm−2 photocurrent densities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...