Facile formation of CoN4 active sites onto a SiO2 support to achieve robust CO2 and proton reduction in a noble-metal-free photocatalytic system†
Abstract
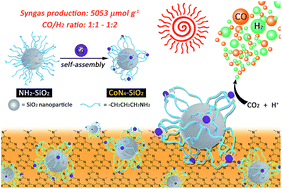
The conversion of CO2 and protons to solar fuels (CO and H2) is the basis of artificial photosynthesis. To date, most of the reported cobalt-based molecular catalysts or single-atom catalysts (SAC) feature a CoN4 core structure. However, the preparation of these metal complex catalysts or SACs requires either a complicated organic ligand synthesis method or harsh material fabrication conditions. In this study, the facile formation of an active CoN4 structure onto a SiO2 support was achieved via self-coordination of Co2+ ions with aminated SiO2 nanoparticles. The formation of the CoN4 structure was identified by synchrotron-based X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The CoN4-SiO2 catalyst exhibited exceptional bifunctional activity of mediating the CO2-to-CO and 2H+-to-H2 conversions in a photochemical system containing g-C3N4 as a photosensitizer. The system robustly produced syngas (CO + H2, CO/H2 = 1 : 1–1 : 2) with a high activity (5053 μmol g−1 and 36 μmol g−1 h−1 based on the catalyst) and remarkable stability (durability > 120 h). Mechanistic studies reveal that the Co(I)-species is the active species generated via a photoinduced electron transfer from g-C3N4 to CoN4-SiO2. The dissociation of Co2+ from the aminated SiO2 support and the decomposition of g-C3N4 under irradiation are the main reasons for the inactivation of the system after long-time photocatalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...