Performance improvement strategies for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells: a review
Abstract
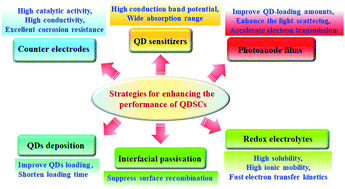
Development of new low-cost technologies for high-efficiency quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSCs) is an effective way to solve current energy and environmental problems. Over the past few years QDSCs employing inorganic semiconductor nanocrystals as the light harvesters, introduced in 2010 with a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 5%, have attracted much attention since the recent breakthrough PCE reports of over 12%. In this review, the strategies to obtain highly efficient QDSCs are discussed in detail from the viewpoints of QD sensitizers, properties of photoanode films, counter electrodes, redox electrolytes, and the interfacial passivation method. Furthermore, the limitations and further prospects are also discussed of how to fabricate QDSC devices with high efficiency and excellent stability. It is expected that these goals can be realized by virtue of the above effective strategies. We believe that this review will not only offer a theoretical basis and technical support for further industrial application of QDSCs, but also provide inspiration and references for performance improvement of other types of solar cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...