Low-voltage alternating current powered polydopamine-protected copper phosphide nanowire for electroporation-disinfection in water†
Abstract
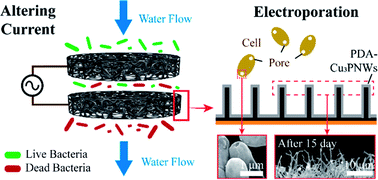
Disinfection is an essential process to protect people from waterborne pathogen infections. Conventional water disinfection methods (e.g., chlorination and ultraviolet radiation) have made considerable contributions to water safety, but are accompanied by obvious drawbacks such as carcinogenic byproduct formation, energy intensiveness, and/or regrowth of pathogens. Here, we develop an electroporation-disinfection cell (EDC) that enables fast water disinfection using a polydopamine-protected copper-phosphide-nanowire-modified copper foam (PDA-Cu3PNW-Cu) electrode powered by a high-frequency alternating current (AC; 106 Hz). Electroporation relies on a strong electric field to damage microorganism membranes without byproduct formation. The PDA film ensures a robust nanowire structure against the hydraulic detachment and reduces mechanical erosion. High-frequency AC as the power source can effectively eliminate electrochemical corrosion and extend the electrode lifetime. EDCs with PDA-Cu3PNW-Cu electrodes achieved complete disinfection (no live microorganism in the effluent) with a low voltage (peak voltage of 1 V) and a high flux (2 m3 h−1 m−2). Under such operating conditions, the PDA-Cu3PNW-Cu electrodes enable complete E. coli disinfection (>6.0 log removal efficiency) for 15 days. To our knowledge, this is the highest value obtained to date for nanostructure-modified electrodes for low-voltage electroporation: 30 times the previously reported maximum lifetime.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...