Changes induced by transition metal oxides in Pt nanoparticles unveil the effects of electronic properties on oxygen reduction activity†
Abstract
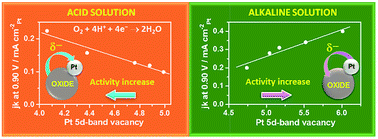
Although the relevance of electronic effects in the electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction has been recognized, the impossibility of separating the effects of composition and particle size for Pt-based materials has hindered establishing clear activity–property relationships. Herein, we report a systematic study based on induced changes via the interactions of pure Pt nanoparticles with transition metal oxide/carbon supports (Pt/MOx/C catalysts, MOx = CeO2, SnO2, TiO2, ZrO2 and WO3). A thorough analysis of aberration-corrected HR-STEM images demonstrated that Pt particles are similar in size and shape for all catalysts, while the direct probing of electronic properties by in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy evidenced charge transfer between Pt and the supports. This approach allowed ascribing the changes in electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction solely to the variations in the electronic vacancy of the Pt 5d band resulting from the interactions between the metal nanoparticles and the supports containing different transition metal oxides. Oxygen reduction was studied in acid and in alkaline solutions, and linear correlations between the kinetic current densities and the Pt 5d band vacancy of pure Pt nanoparticles were found in both media. Possible first steps of the reduction of oxygen are discussed to explain the trends observed. The results, evidencing that enhanced ORR activity on Pt particles is promoted by a lower 5d band vacancy in acid solutions and by a higher one in alkaline medium, provide new insights on the fundamental aspects of oxygen reduction, and open up new possibilities to develop catalysts with enhanced activity for fuel cell cathodes by tuning their electronic properties.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Celebrating Latin American Talent in Chemistry and Materials and Nano Research in Brazil


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...