Biophysical investigation into the antibacterial action of modelin-5-NH2
Abstract
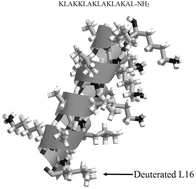
Modelin-5-CONH2 (M5-NH2) is a synthetic antimicrobial peptide, which was found to show potent activity against Bacillus subtilis (minimum lethal concentration = 8.47 μM) and to bind strongly to membranes of the organism (Kd = 10.44 μM). The peptide adopted high levels of amphiphilic α-helical structure in the presence of these membranes (>50%), which led to high levels of insertion (Δπ ≥ 8.0 mN m−1). M5-NH2 showed high affinity for anionic lipid (Kd = 7.46 μM) and zwitterionic lipid (Kd = 14.7 μM), which drove insertion into membranes formed from these lipids (Δπ = 11.5 and 3.5 mN m−1, respectively). Neutron diffraction studies showed that M5-NH2 inserted into B. subtilis membranes with its N-terminal residue, L16, located 5.5 Å from the membrane centre, in the acyl chain region of these membranes, and promoted a reduction in membrane thickness of circa 1.8 Å or 5% of membrane width. Insertion into B. subtilis membranes by the peptide also promoted other effects associated with membrane thinning, including increases in membrane surface area (Cs−1 decreases) and fluidity (ΔGmix > 0 to ΔGmix < 0). Membrane insertion and thinning by M5-NH2 induced high levels of lysis (>55%), and it is speculated that the antibacterial action of the peptide may involve the toroidal pore, carpet or tilted-type mechanism of membrane permeabilization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...