Hydrogenolysis of biorefinery corncob lignin into aromatic phenols over activated carbon-supported nickel†
Abstract
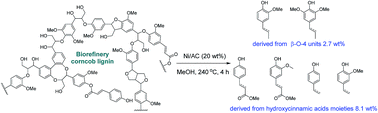
Lignin is the most abundant renewable resource for production of bio-aromatic chemicals. However, the catalytic depolymerisation of lignin into phenolic monomers is still challenging due to its intrinsic heterogeneity. Herein, we report that Ni/AC can serve as an efficient and stable catalyst in the hydrogenolysis of biorefinery corncob lignin into low-molecular-weight aromatics. This catalyst showed high activity towards reductive fragmentation of hydroxycinnamic esters and β-O-4 linkages through scission by reaction with hydrogen to cleave C–O bonds. Under optimal conditions, this catalytic system produced 31% selectivity towards unsaturated substituents containing coumarate and ferulate derivatives, which afforded mono-aromatic phenols (up to 12.1 wt%) derived from hydroxycinnamic acid moieties (8.1 wt%) and β-O-4 units (2.7 wt%), respectively. The use of non-precious metals to develop highly efficient heterogeneous catalysts makes this approach of great interest in the production of aromatic phenols for the valorisation of industrial lignin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...