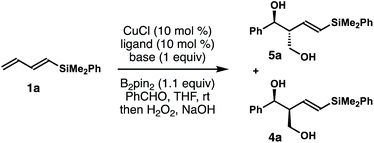Open Access Article
Open Access Articleα-Silicon effect assisted Curtin–Hammett allylation using allylcopper reagents derived from 1,3-dienylsilanes†
Shang
Gao
and
Ming
Chen
 *
*
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849, USA. E-mail: mzc0102@auburn.edu
First published on 28th June 2019
Abstract
Cu-catalyzed stereoselective synthesis of (E)-δ-silyl-anti-homoallylic alcohols from 1,3-dienylsilane was developed. Mechanistic studies revealed that the borocupration of dienylsilane proceeded through a 1,2-addition pathway to give an allylcopper intermediate with Cu distal to the silyl group. However, the subsequent aldehyde allylation proceeded via Curtin–Hammett control to give (E)-δ-silyl-anti-homoallylic alcohols with high diastereoselectivities. This method was applied to the synthesis of the C1–9 fragment of a polyketide natural product, mycinolide IV.
Introduction
Stereoselective transformation of carbon–carbon multiple bonds catalyzed by transition-metal complexes is a powerful approach to generate molecular complexity from structurally simple π-bonds.1 In particular, reactions employing 1,3-conjugated dienes are attractive because of multiple potential reaction pathways that can be involved in these processes. By proper selection of the catalyst/ligand combination, distinct products can be generated with high selectivities from these reactions.2 Such processes are valuable because they can often form several chemical bonds, generate several stereocenters, and provide highly useful intermediates for chemical synthesis. Over the past several decades, significant advances in stereoselective transformation of 1,3-conjugated dienes,3–7 enynes and allenes as well have been achieved,8 and many highly innovative strategies have been developed.Recently, transition-metal catalyzed reactions of 1,3-conjugated dienes with carbonyl compounds have emerged as an important method to synthesize alcohol products.9–11 Synthetically valuable homoallylic alcohols in particular12 can be produced from 1,3-conjugated dienes with high stereoselectivities.10 The Krische group demonstrated that allyl-Ru intermediates, which can be catalytically generated from 1,3-butadiene, reacted with aldehydes to furnish homoallylic alcohols with high enantiopurities.10 Ni-catalyzed borylative 1,3-diene-aldehyde coupling, developed by the Morken group, proceeds through a different mechanism to produce homoallylic alcohols with high diastereoselectivities.11 By contrast, Cu-catalyzed reactions using 1,3-conjugated dienes and carbonyl compounds received much less attention.13 Liao and co-workers reported a three-component coupling of 1,3-butadiene, B2pin2 and imines to generate syn-homoallylic amines.13a The Yu group recently showed a Cu-catalyzed reductive hydroxymethylation of 1,3-dienes with CO2 and silane.13b And Cu-catalyzed enantioselective reductive coupling of ketones with 2-azadienes and dienes was disclosed by Malcolmson and Buchwald.13c,d
While 1,3-butadiene and aryl-substituted 1,3-butadiene were employed in these studies, we were intrigued whether 1,3-dienylsilanes can be used to produce silyl substituted homoallylic alcohols. With our continuing interest in carbonyl allylation chemistry,14 we herein report a Cu-catalyzed stereoselective synthesis of (E)-δ-silyl-anti-homoallylic alcohols from B2pin2, aldehydes and 1,3-dienylsilanes. A notable feature of this method is that the homoallylic alcohol products obtained from the reactions contain a stereochemically defined 1,3-diol unit, and an E-vinyl silane group that is amenable to a variety of subsequent transformations. Mechanistic studies revealed that the reaction proceeded through 1,2-borocupration of the terminal alkene unit to generate an allylcopper intermediate, with Cu residing distal to the silyl group. Subsequent aldehyde allylation occurred under Curtin–Hammett control to give homoallylic alcohol products with high selectivities.
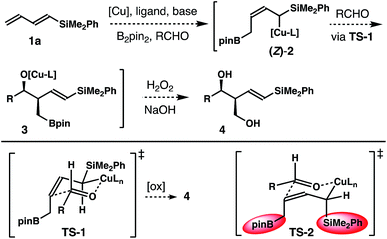
Results and discussion
Inspired by recent studies on Cu–B addition to carbon–carbon multiple bonds15 and allylcopper chemistry,16–18 we envisioned a Cu-catalyzed reaction of dienylsilane, B2pin2 and an aldehyde to synthesize δ-silyl-homoallylic alcohols. As shown in Scheme 1, we anticipated that in situ generated, monodentate ligand-bound Cu–Bpin species would undergo 1,4-borocupration of dienylsilane 1a to form an allylcopper intermediate (Z)-2 first. It is conceivable that the kinetic product (Z)-2 could undergo reversible 1,3-metalloshifts to give an (E)-isomer that is thermodynamically more stable. However, we surmised that such 1,3-metalloshifts might be slow owing to the electronic stabilization provided by the neighbouring –SiMe2Ph group (silicon α-anion effect).19 Subsequent nucleophilic addition of the allyl-Cu intermediate (Z)-2 to aldehyde substrates17,18 should proceed through the well-established Zimmerman–Traxler transition state20 (TS-1, Scheme 1) to produce (E)-δ-silyl-syn-homoallylic alcohol products 4 upon oxidative workup. The competing transition state for the allyl addition step, TS-2, which would lead to the formation of a (Z)-olefin isomer, suffers from a severe A1,3 allylic strain (shown in red in TS-2)21 and therefore is disfavoured. Consequently, the formation of syn-homoallylic alcohols 4 was anticipated from this reaction sequence.To implement the proposed strategy, we initiated our studies to identify suitable conditions for the stereoselective reaction of dienylsilane 1a, B2pin2 and benzaldehyde (Table 1). The initial experiments were conducted in the presence of 10 mol% CuCl and a ligand, 1.0 equiv. of dienylsilane 1a, 1.0 equiv. of a base, 1.1 equiv. of B2pin2 and 1.2 equiv. of benzaldehyde in THF at ambient temperature. Surprisingly, when a monodentate NHC ligand IPr·HCl was utilized with NaOt-Bu as the base, the reaction did not produce any detectable amount of the product (entry 1, Table 1). The reaction with IMes·HCl as the ligand and NaOt-Bu as the base, however, generated a 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of 5a and 4a in 21% yield (entry 2). In contrast to the anticipated syn relative configuration, the major product 5a is an anti-isomer as determined by coupling constant analysis of the corresponding acetonide derivative (please see the ESI† for details). The reaction with SICy·HCl as the ligand precursor gave inferior results (entry 3). Next, reactions with a bidentate phosphor ligand were conducted. The reaction with dppbz as the ligand produced a 3
1 mixture of 5a and 4a in 21% yield (entry 2). In contrast to the anticipated syn relative configuration, the major product 5a is an anti-isomer as determined by coupling constant analysis of the corresponding acetonide derivative (please see the ESI† for details). The reaction with SICy·HCl as the ligand precursor gave inferior results (entry 3). Next, reactions with a bidentate phosphor ligand were conducted. The reaction with dppbz as the ligand produced a 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of 5a and 4a in 32% yield (entry 4). The diastereoselectivity was improved to 10
1 mixture of 5a and 4a in 32% yield (entry 4). The diastereoselectivity was improved to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 when Xantphos was utilized (entry 5). A brief evaluation of the base such as LiOt-Bu or KOt-Bu showed either a lower yield or selectivity (entries 6 and 7). While modification of the base was not fruitful, the yield of reaction was improved to 77% at the expense of diastereoselectivity with toluene as the solvent (entry 8). The reaction did not occur in the absence of any base or ligand (entries 9 and 10). Gratifyingly, we discovered that when Cu(OMe)2 was employed as the catalyst in lieu of CuCl, the reaction provided a 14
1 when Xantphos was utilized (entry 5). A brief evaluation of the base such as LiOt-Bu or KOt-Bu showed either a lower yield or selectivity (entries 6 and 7). While modification of the base was not fruitful, the yield of reaction was improved to 77% at the expense of diastereoselectivity with toluene as the solvent (entry 8). The reaction did not occur in the absence of any base or ligand (entries 9 and 10). Gratifyingly, we discovered that when Cu(OMe)2 was employed as the catalyst in lieu of CuCl, the reaction provided a 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of 5a and 4a in 87% yield without the addition of any base (entry 11).22 Again, the presence of the xantphos ligand is crucial; the reaction in the absence of xantphos failed to provide any product with Cu(OMe)2 as the catalyst, which suggests that the ligand-bound Cu-complex is the active catalyst for this reaction (entry 12).
1 mixture of 5a and 4a in 87% yield without the addition of any base (entry 11).22 Again, the presence of the xantphos ligand is crucial; the reaction in the absence of xantphos failed to provide any product with Cu(OMe)2 as the catalyst, which suggests that the ligand-bound Cu-complex is the active catalyst for this reaction (entry 12).
| Entry | Ligand | Base |
Anti![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) synb synb |
Yield (4a + 5a)c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Reaction conditions: dienylsilane 1a (0.1 mmol, 1 equiv.), CuCl (10 mol%), ligand (10 mol%), base (0.1 mmol, 1 equiv.), B2pin2 (0.11 mmol, 1.1 equiv.), benzaldehyde (0.12 mmol, 1.2 equiv.), and THF (0.3 mL); rt, 12 h. b The anti/syn and E/Z ratios were determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction products. c Yields of isolated products are listed. d The reaction was conducted in toluene. e Cu(OMe)2 (10 mol%) was used as the catalyst. | ||||
| 1 | IPr·HCl | NaOt-Bu | N.D. | N.R. |
| 2 | IMes·HCl | NaOt-Bu | 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
21 |
| 3 | SICy·HCl | NaOt-Bu | 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
19 |
| 4 | dppbz | NaOt-Bu | 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
32 |
| 5 | Xantphos | NaOt-Bu | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
40 |
| 6 | Xantphos | LiOt-Bu | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
26 |
| 7 | Xantphos | KOt-Bu | 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
61 |
| 8d | Xantphos | NaOt-Bu | 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
77 |
| 9 | No ligand | NaOt-Bu | N.D. | N.R. |
| 10 | Xantphos | No base | N.D. | N.R. |
| 11e | Xantphos | No base | 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
87 |
| 12e | No ligand | No base | N.D. | N.R. |
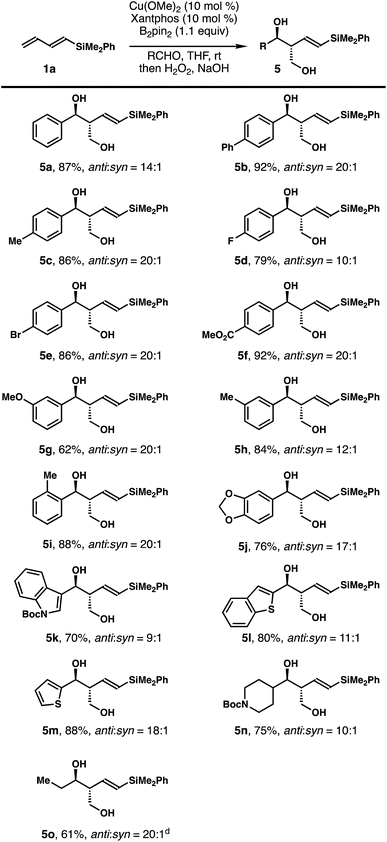
The scope of the aldehyde that participated in the reactions with dienylsilane 1a is summarized in Table 2. In general, the reaction worked well with a variety of aldehydes. For example, aromatic aldehydes with substitution at the para-position regardless of the electronic properties reacted to give products 5a–f in 79–92% yields with 10–20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 anti/syn ratios. Reactions with aromatic aldehydes substituted at the meta- or ortho-position proceeded to provide alcohols 5g–j in 62–88% yields with 12–20
1 anti/syn ratios. Reactions with aromatic aldehydes substituted at the meta- or ortho-position proceeded to provide alcohols 5g–j in 62–88% yields with 12–20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 diastereoselectivities. Reactions with heteroaromatic aldehydes proceeded smoothly to deliver diols 5k–m in 70–88% yields with 9–18
1 diastereoselectivities. Reactions with heteroaromatic aldehydes proceeded smoothly to deliver diols 5k–m in 70–88% yields with 9–18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 diastereoselectivities. Finally, aliphatic aldehydes participated in the reaction as well to give products 5n–o in 61–75% yields with 10–20
1 diastereoselectivities. Finally, aliphatic aldehydes participated in the reaction as well to give products 5n–o in 61–75% yields with 10–20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 anti/syn ratios. The olefin geometry of alcohols 5 was assigned as E based on 1H NMR analysis of the coupling constant of olefinic protons.
1 anti/syn ratios. The olefin geometry of alcohols 5 was assigned as E based on 1H NMR analysis of the coupling constant of olefinic protons.
| a Reaction conditions: diene 1a (0.1 mmol, 1 equiv.), Cu(OMe)2 (10 mol%), Xantphos (10 mol%), B2pin2 (0.11 mmol, 1.1 equiv.), aldehyde (0.12 mmol, 1.2 equiv.), and THF (0.3 mL); rt, 12–48 h. b Diastereoselectivities were determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction products. c Yields of isolated products are listed. d Reactions were conducted at 0 °C. |
|---|
|
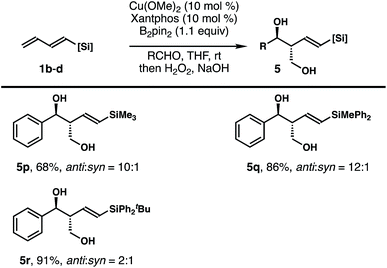
To probe whether the size of the silyl group of 1,3-diene has any impact on the stereochemical outcomes of the reaction, dienylsilanes 1b–d substituted with a different sized silyl group were synthesized, and reactions with these dienylsilanes under the developed conditions were conducted. As shown in Table 3, the reaction of less sterically demanding trimethylsilyl substituted 1,3-diene 1b with benzaldehyde under standard conditions afforded the diol product 5p in 68% yield with 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 anti/syn selectivity. Diphenylmethylsilyl substituted 1,3-diene 1c also reacted to generate product 5q in 86% yield with 12
1 anti/syn selectivity. Diphenylmethylsilyl substituted 1,3-diene 1c also reacted to generate product 5q in 86% yield with 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 anti/syn selectivity. The reaction of benzaldehyde with a much more sterically demanding –SiPh2tBu substituted 1,3-diene 1d under standard conditions provided diol 5r as a 2
1 anti/syn selectivity. The reaction of benzaldehyde with a much more sterically demanding –SiPh2tBu substituted 1,3-diene 1d under standard conditions provided diol 5r as a 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of anti and syn isomers in 91% combined yield, with the anti adduct as the major product. In all cases, the formation of any isomer with Z-olefin geometry was not observed. Overall, the results indicate that the size of the silyl group of 1,3-diene does affect the anti/syn selectivity of the reaction, particularly in the case of the bulky SiPh2tBu group substituted 1,3-diene 1d.
1 mixture of anti and syn isomers in 91% combined yield, with the anti adduct as the major product. In all cases, the formation of any isomer with Z-olefin geometry was not observed. Overall, the results indicate that the size of the silyl group of 1,3-diene does affect the anti/syn selectivity of the reaction, particularly in the case of the bulky SiPh2tBu group substituted 1,3-diene 1d.
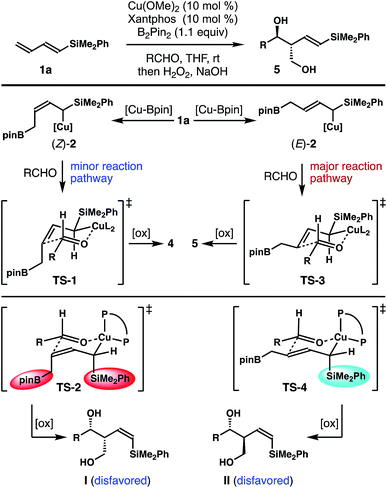
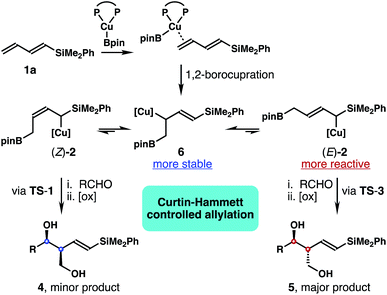
It has been well-established that the addition of allyl copper species to aldehyde proceeded by way of a 6-membered, chair-like transition state.16,20 Therefore, the anti relative stereochemistry of homoallylic alcohols 5 suggests that the dominant reaction pathway of aldehyde addition is through the allylcopper intermediate (E)-2 (Scheme 2). The reaction of aldehyde with isomer (Z)-2 is only a minor pathway. As shown in Scheme 2, the minor reaction pathway involves the addition of (Z)-2 to an aldehyde viaTS-1 to give the syn-isomer 4 because the competing transition state TS-2 suffers from a severe A1,3 allylic strain (shown in red in TS-2).21 Therefore, the formation of the (Z)-homoallylic alcohol product I was disfavoured, and only the syn-adduct 4 was formed in this minor reaction pathway. On the other hand, the addition of (E)-2 to the aldehyde proceeded through a transition state TS-3 to deliver alcohol 5 as the product in the major reaction pathway. It is worth noting that, although the competing transition state TS-4 lacks A1,3 allylic strains, the reaction of (E)-2 with an aldehyde did not proceed through TS-4 with pseudo axial placement of the –SiMe2Ph group in the transition state (shown in light blue in TS-4) to provide product II with Z-olefin geometry (alcohol II was not detected from the reaction). Instead, –SiMe2Ph was oriented in the pseudo equatorial position in TS-3 to give product 5 with E-olefin geometry. Based on the studies of stereoelectronic effects in allylboration chemistry conducted by Hoffmann,23 σ–π* delocalization between the σ-orbital of the C–Si single bond and the π*-orbital of the olefin unit in TS-3 is presumably responsible for the observed E-alkene stereoselectivity in product 5. In addition to the stereoelectronic effect, the large –SiMe2Ph group occupying a pseudo equatorial position in the transition state TS-3 could also make TS-3 more favourable than TS-4.
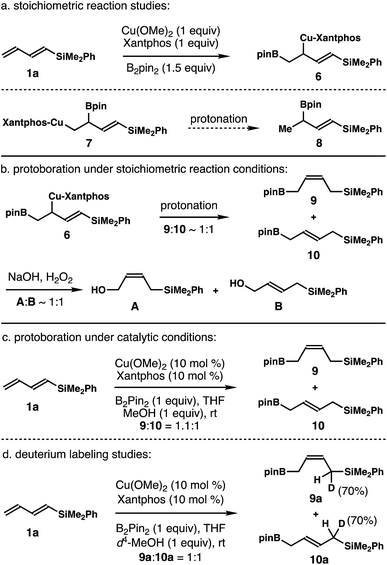
Although the data indicate that the dominant reaction pathway of aldehyde addition is through the allylcopper intermediate (E)-2 (Scheme 2), it is not clear whether allylcopper (E)-2 was generated as the major product from the addition of Xantphos-ligated Cu–Bpin species to dienylsilane 1a. To gain mechanistic insight into this process, stoichiometric reaction studies with dienylsilane 1a were conducted. As shown in the top panel of Scheme 3, 1 equiv. of Cu(OMe)2, Xantphos (1 equiv.), dienylsilane 1a (1 equiv.), and B2pin2 (1.5 equiv.) were stirred at ambient temperature, and the reaction progress was monitored by 1H-NMR spectroscopy until dienylsilane 1a was completely consumed. Surprisingly, we only observed one set of two olefinic proton signals (dd, J = 18.7 Hz and d, J = 18.7 Hz), which corresponds to a characteristic vinylsilane group with a methine group adjacent to one vinyl proton. Proton signals corresponding to either (E)-2 or (Z)-2 were not detected. The data indicate that the allylcopper species generated from the initial Cu–Bpin addition to diene 1a should be a 1,2-borocupration adduct, 6 or 7 (Scheme 3a).
To determine which 1,2-addition product, 6 or 7, was generated from the reaction, protonation of the intermediate obtained from stoichiometric borocupration of diene 1a was performed. As shown in Scheme 3a, protonation of the intermediate formed via the stoichiometric reaction did not produce any detectable amount of the boronate intermediate 8, which would be the product from protonation of intermediate 7. Instead, a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylboronates 9 and 10 was generated through a SE2′ pathway from allylcopper species 6 (Scheme 3b). A direct SE2 protonation product from 6 was not observed. Oxidation studies further corroborated the identity of 9 and 10 as a 1
1 mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylboronates 9 and 10 was generated through a SE2′ pathway from allylcopper species 6 (Scheme 3b). A direct SE2 protonation product from 6 was not observed. Oxidation studies further corroborated the identity of 9 and 10 as a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylic alcohols, A and B, was formed upon oxidation (Scheme 3b). Protoboration studies of dienylsilane 1a under the developed catalytic conditions were also conducted. As shown in Scheme 3c, the reaction of dienylsilane 1a with 1 equiv. of B2pin2 and 1 equiv. of MeOH in the presence of 10 mol% Cu(OMe)2 and 10 mol% Xantphos ligand provided a 1.1
1 mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylic alcohols, A and B, was formed upon oxidation (Scheme 3b). Protoboration studies of dienylsilane 1a under the developed catalytic conditions were also conducted. As shown in Scheme 3c, the reaction of dienylsilane 1a with 1 equiv. of B2pin2 and 1 equiv. of MeOH in the presence of 10 mol% Cu(OMe)2 and 10 mol% Xantphos ligand provided a 1.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylboronates 9 and 10. Again, the formation of allylboronate 8 was not detected. Finally, deuterium-labeling studies of dienylsilane 1a were conducted with d4-MeOH under the developed catalytic conditions. As shown in Scheme 3d, the reaction of 1a in the presence of 1 equiv. of d4-MeOH provided a 1
1 mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylboronates 9 and 10. Again, the formation of allylboronate 8 was not detected. Finally, deuterium-labeling studies of dienylsilane 1a were conducted with d4-MeOH under the developed catalytic conditions. As shown in Scheme 3d, the reaction of 1a in the presence of 1 equiv. of d4-MeOH provided a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 inseparable mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylboronates 9a and 10a with 70% deuterium incorporation at the positions α to the –SiMe2Ph group. These data further support the SE2′ protonation pathway of allylcopper intermediate 6 to give allylboronates 9 and 10.
1 inseparable mixture of (Z)- and (E)-allylboronates 9a and 10a with 70% deuterium incorporation at the positions α to the –SiMe2Ph group. These data further support the SE2′ protonation pathway of allylcopper intermediate 6 to give allylboronates 9 and 10.
These data clearly demonstrate that the most stable allylcopper intermediate generated from the initial borocupration is the 1,2-adduct 6 with copper residing distal to the –SiMe2Ph group, not the speculated allylcopper (E)-2 or (Z)-2 as shown in Scheme 2. Presumably the steric interaction between the Cu–Xantphos group and the –SiMe2Ph group (as in either (E)-2 or (Z)-2 shown in Scheme 2) is too severe to overcome by the stereoelectronic stabilization from the –SiMe2Ph group. By contrast, the results in Tables 1 and 2 indicate that the major reactive intermediate in the reactions is allylcopper (E)-2, and we were not able to detect any allylation product derived from allylcopper 6.25 Therefore, we conclude that (1) the activation energy for the addition of allylcopper species (E)-2 to aldehyde is much lower than that of allylcopper species 6; (2) a fast equilibrium exists among allylcopper intermediates (E)-2, (Z)-2 and 6 through facile 1,3-metallo shifts; (3) the rate of equilibration among (E)-2, (Z)-2 and 6 is much faster than that of allylation with aldehydes.
Based on the data obtained from these studies, we propose the following reaction pathway. As illustrated in Scheme 4, the in situ generated Xantphos–Cu–Bpin species coordinates to the terminal alkene unit of dienylsilane 1a to form a Cu–olefin complex. Subsequent borylcupration24 of diene 1a occurred in a 1,2-addition pathway to give intermediate 6 as the most stable allylcopper species. Although 6 was generated as the predominant allylcopper species from the initial 1,2-borylcupration, the addition to the aldehyde did not occur via allylcopper 6. Instead, intermediate 6 equilibrates with (E)-2 and (Z)-2via rapid and reversible 1,3-metalloshifts,25 and subsequent nucleophilic addition to the aldehyde proceeded via the more reactive allylcopper (E)-2.26 Therefore, intermediate 6 is funnelled to allylcopper (E)-2 under Curtin–Hammett control27 to generate the anti-adduct 5 from the allylation. Presumably the stereoelectronic benefit from the σ–π* delocalization of the α-silyl group makes TS-3 the lowest energy transition state for the allylation.
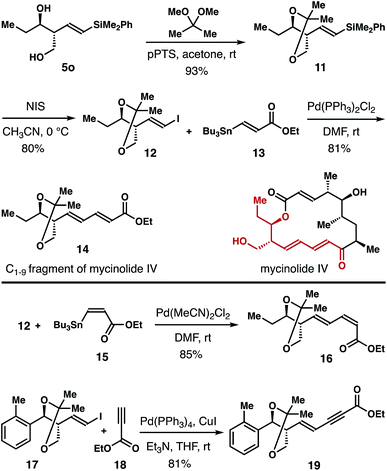
The homoallylic alcohol product 5 obtained from the reaction is highly valuable because it contains a stereochemically defined 1,3-diol unit, and a vinyl silane group that is amenable to a variety of subsequent transformations.28 Synthetic applications of this method are shown in Scheme 5. Diol 5o was converted into acetonide 11 in 93% yield. Then acetonide 11 was transformed into vinyl iodide 12 in 80% yield with NIS as the iodination reagent. Pd-catalyzed Stille-coupling of vinyl iodide 12 with (E)-vinyl stannane 13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 29 gave product 14 in 81% yield, which corresponds to the C1–9 fragment of the polyketide natural product mycinolide IV. In addition, Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling of 12 and (Z)-vinyl stannane 15
29 gave product 14 in 81% yield, which corresponds to the C1–9 fragment of the polyketide natural product mycinolide IV. In addition, Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling of 12 and (Z)-vinyl stannane 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 delivered diene 16 in 85% yield. Sonogashira coupling of 17 with ethyl propiolate (18) furnished enyne 19 in 81% yield.31
30 delivered diene 16 in 85% yield. Sonogashira coupling of 17 with ethyl propiolate (18) furnished enyne 19 in 81% yield.31
Conclusions
In summary, we developed Cu-catalyzed diastereoselective synthesis of (E)-δ-silyl-anti-homoallylic alcohols from 1,3-dienylsilanes.32 Mechanistic studies revealed that the borocupration proceeded through a 1,2-addition pathway to give the allylcopper intermediate 6 as the most stable allylcopper species. However, the allylcopper intermediate 6 was funnelled to more reactive allylcopper species (E)-2via reversible 1,3-metallo shifts under Curtin–Hammett control in the subsequent aldehyde allylation step to give (E)-δ-silyl-anti-homoallylic alcohols with high diastereoselectivity. The α-silicon effect is proposed to be the underlying driving force for the observed selectivity. This method was applied to the synthesis of the C1–9 fragment of a polyketide natural product mycinolide IV. Other synthetic applications of this method will be reported in due course.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Financial support provided by Auburn University is gratefully acknowledged. We thank AllylChem for generously gifting B2pin2.Notes and references
- For selected recent reviews: (a) H. C. Kolb, M. S. VanNieuwenhze and K. B. Sharpless, Chem. Rev., 1994, 94, 2483 CrossRef CAS; (b) F. Agbossou, J.-F. Carpentier and A. Mortreux, Chem. Rev., 1995, 95, 2485 CrossRef CAS; (c) I. Beletskaya and C. Moberg, Chem. Rev., 1999, 99, 3435 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) E. M. McGarrigle and D. G. Gilheany, Chem. Rev., 2005, 105, 1563 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) T. E. Müller, K. C. Hultzsch, M. Yus, F. Foubelo and M. Tada, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 3795 CrossRef PubMed; (f) O. A. Wong and Y. Shi, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 3958 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) F. Hebrard and P. Kalck, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 4272 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) M. C. Willis, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 725 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) R. I. McDonald, G. Liu and S. S. Stahl, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 2981 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) Y. Zhu, Q. Wang, R. G. Cornwall and Y. Shi, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 8199 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Holmes, L. A. Schwartz and M. J. Krische, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 6026 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Suginome, H. Nakamura, T. Matsuda and Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 4248 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Shirakura and M. Suginome, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 5410 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. Shirakura and M. Suginome, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 3827 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) H. E. Burks, L. T. Kliman and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 9134 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) R. J. Ely and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 2534 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) C. H. Schuster, B. Li and J. P. Morken, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 7906 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Z. Yu, R. J. Ely and J. P. Morken, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 9632 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) X.-H. Yang and V. M. Dong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 1774 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X.-H. Yang, A. Lu and V. M. Dong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 14049 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) X.-H. Yang, R. Davison and V. M. Dong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 10443 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) S.-Z. Nie, R. T. Davison and V. M. Dong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 16450 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. S. McCammant, L. Liao and M. S. Sigman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 4167 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) V. Saini, M. O'Dair and M. S. Sigman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 608 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) Y. Yang, S.-F. Zhu, H.-F. Duan, C.-Y. Zhou, L.-X. Wang and Q.-L. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 2248 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. Y. Wu, B. Moreau and T. Ritter, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 12915 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Xiong and G. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 2735 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) K. B. Smith and M. K. Brown, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 7721 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. R. Sardini and M. K. Brown, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 9823 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For selected recent examples on transition metal-catalyzed carbonyl additions involving 1,3-enynes: (a) L. M. Geary, S. K. Woo, J. C. Leung and M. J. Krische, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2972 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) F. Meng, F. Haeffner and A. H. Hoveyda, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 11304 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Yang, I. B. Perry, G. Lu, P. Liu and S. L. Buchwald, Science, 2016, 353, 144 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) K. D. Nguyen, D. Herkommer and M. J. Krische, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 5238 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) X.-C. Gan, Q. Zhang, X.-S. Jia and L. Yin, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 1070 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) X.-C. Gan and L. Yin, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 931 CrossRef CAS PubMed; For selected recent examples on transition metal-catalyzed carbonyl additions involving allenes: (g) J. Rae, K. Yeung, J. J. W. McDouall and D. J. Procter, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 1102 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) K. Yeung, R. E. Ruscoe, J. Rae, A. P. Pulis and D. J. Procter, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 11912 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) T. Fujihara, A. Sawada, T. Yamaguchi, Y. Tani, J. Terao and Y. Tsuji, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 1539 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) A. Boreux, K. Indukuri, F. Gagosz and O. Riant, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 8200 CrossRef CAS; (k) A. Sawada, T. Fujihara and Y. Tsuji, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2018, 360, 2621 CrossRef CAS; (l) R. Y. Liu, Y. Zhou, Y. Yang and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 2251 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Kimura, A. Ezoe, K. Shibata and Y. Tamaru, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 4033 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Kimura, H. Fujimatsu, A. Ezoe, K. Shibata, M. Shimizu, S. Matsumoto and Y. Tamaru, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1999, 38, 397 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Kimura, S. Matsuo, K. Shibata and Y. Tamaru, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1999, 38, 3386 CrossRef CAS; (d) Y. Sato, M. Takimoto and M. Mori, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 1624 CrossRef CAS; (e) Y. Sato, N. Saito and M. Mori, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 2371 CrossRef CAS; (f) S. Ogoshi, K.-i. Tonomori, M.-a. Oka and H. Kurosawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 7077 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) M. Kimura, A. Ezoe, M. Mori, K. Iwata and Y. Tamaru, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 8559 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. R. Zbieg, E. Yamaguchi, E. L. McInturff and M. J. Krische, Science, 2012, 336, 324 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. L. McInturff, E. Yamaguchi and M. J. Krische, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 20628 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. D. Nguyen, D. Herkommer and M. J. Krische, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 14210 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) H. Y. Cho and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 16140 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Y. Cho and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 7576 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) L. T. Kliman, S. N. Mlynarski, G. E. Ferris and J. P. Morken, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 521 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) G. E. Ferris, K. Hong, I. A. Roundtree and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 2501 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Feng, Z. A. Kasun and M. J. Krische, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 5467 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) L. Jiang, P. Cao, M. Wang, B. Chen, B. Wang and J. Liao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 13854 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y.-Y. Gui, N. Hu, X.-W. Chen, L.-L. Liao, T. Ju, J.-H. Ye, Z. Zhang, J. Li and D.-G. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 17011 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. Li, X. Shao, L. Tseng and S. J. Malcolmson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 598 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) C. Li, R. Y. Liu, L. T. Jesikiewicz, Y. Yang, P. Liu and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 5062 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Wang, S. Khan, E. Miliordos and M. Chen, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 3810 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Gao and M. Chen, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 6174 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. Wang, S. Khan, E. Miliordos and M. Chen, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2018, 360, 4634 CrossRef CAS; (d) S. Gao, M. Wang and M. Chen, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 7921 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. Gao, J. Chen and M. Chen, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 3637 RSC; (f) M. Wang, S. Gao and M. Chen, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 2151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For selected reviews: (a) J. Yun, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2013, 2, 1016 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. Barbeyron, E. Benedetti, J. Cossy, J.-J. Vasseur, S. Arseniyadis and M. Smietana, Tetrahedron, 2014, 70, 8431 CrossRef CAS; (c) Y. Shimizu and M. Kanai, Tetrahedron Lett., 2014, 55, 3727 CrossRef CAS; (d) K. Semba, T. Fujihara, J. Terao and Y. Tsuji, Tetrahedron, 2015, 71, 2183 CrossRef CAS; (e) E. C. Neeve, S. J. Geier, I. A. I. Mkhalid, S. A. Westcott and T. B. Marder, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 9091 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) H. Yoshida, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 1799 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Shibasaki and M. Kanai, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 2853 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) S. Yamasaki, K. Fujii, R. Wada, M. Kanai and M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 6536 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. Wada, K. Oisaki, M. Kanai and M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 8910 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) R. Wada, T. Shibuguchi, S. Makino, K. Oisaki, M. Kanai and M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 7687 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. Kanai, R. Wada, T. Shibuguchi and M. Shibasaki, Pure Appl. Chem., 2008, 80, 1055 CAS; (e) S.-L. Shi, L.-X. Xu, K. Oisaki, M. Kanai and M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 6638 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For selected recent examples of Cu-catalyzed asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions: (a) R. Yazaki, N. Kumagai and M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 3195 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) R. Yazaki, N. Kumagai and M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 5522 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) D. R. Fandrick, K. R. Fandrick, J. T. Reeves, Z. Tan, W. Tang, A. G. Capacci, S. Rodriguez, J. J. Song, H. Lee, N. K. Yee and C. H. Senanayake, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 7600 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) K. R. Fandrick, D. R. Fandrick, J. T. Reeves, J. Gao, S. Ma, W. Li, H. Lee, N. Grinberg, B. Lu and C. H. Senanayake, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 10332 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) X.-F. Wei, X.-W. Xie, Y. Shimizu and M. Kanai, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 4647 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) A. R. Bassindale and P. G. Taylor, in The chemistry of organic silicon compounds, ed. S. Patai and Z. Rappoport, Wiley, New York, 1989; p. 893 Search PubMed; (b) T. H. Chan and D. Wang, Chem. Rev., 1995, 95, 1279 CrossRef CAS; (c) G. A. Gornowicz and R. West, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1968, 90, 4478 CrossRef CAS; (d) C. H. DePuy, V. M. Bierbaum, L. A. Flippin, J. J. Grabowski, G. K. King, R. J. Schmitt and S. A. Sullivan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1980, 102, 5012 CrossRef CAS; (e) P. V. R. Schleyer, T. Clark, A. J. Kos, G. W. Spitznagel, C. Rohde, D. Arad, K. N. Houk and N. G. Rondan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1984, 106, 6467 CrossRef CAS; (f) D. M. Wetzel and J. I. Brauman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1988, 110, 8333 CrossRef CAS; (g) E. A. Brinkman, S. Berger and J. I. Brauman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 8304 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) H. E. Zimmerman and M. D. Traxler, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1957, 79, 1920 CrossRef CAS; (b) Although boat-like transition states cannot be ruled out, chair-like transition states are proposed in all prior studies on allyl-copper addition to carbonyl compounds.
- (a) R. W. Hoffmann, Chem. Rev., 1989, 89, 1841 CrossRef CAS. For recent examples: (b) M. Althaus, A. Mahmood, J. R. Suárez, S. P. Thomas and V. K. Aggarwal, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 4025 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. Chen and W. R. Roush, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 2706 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) J.-L. Han, M. Chen and W. R. Roush, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 3028 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) B. Potter, A. A. Szymaniak, E. K. Edelstein and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 17918 CrossRef CAS.
- The effect of methoxide vs. tert-butoxide on the diastereoselectivity of the reaction is not clear at the moment. It is a subject for future studies.
- R. W. Hoffmann and J. J. Wolff, Chem. Ber., 1991, 124, 563 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) Y. Sasaki, C. Zhong, M. Sawamura and H. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 1226 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. Semba, M. Shinomiya, T. Fujihara, J. Terao and Y. Tsuji, Chem.–Eur. J., 2013, 19, 7125 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Addition of allylcopper 6 generated from the stoichiometric reaction to benzaldehyde produced a 1
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 mixture of 5a and 4a. These data are consistent with the fast equilibrium among 6, (E)-2 and (Z)-2via reversible 1,3-metalloshifts. Although 6 was generated as the only observed allylcopper intermediate from the stoichiometric reaction, any allylation product derived from 6 was not detected. These data also indicate that the activation energy for the addition of allylcopper 6 to an aldehyde is much higher than those of (E)-2 and (Z)-2.
3 mixture of 5a and 4a. These data are consistent with the fast equilibrium among 6, (E)-2 and (Z)-2via reversible 1,3-metalloshifts. Although 6 was generated as the only observed allylcopper intermediate from the stoichiometric reaction, any allylation product derived from 6 was not detected. These data also indicate that the activation energy for the addition of allylcopper 6 to an aldehyde is much higher than those of (E)-2 and (Z)-2. - (E)-Allylation reagents are generally more reactive than (Z)-isomers toward aldehyde addition. For recent references, see: (a) T. Miura, J. Nakahashi and M. Murakami, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 6989 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) T. Miura, J. Nakahashi, W. Zhou, Y. Shiratori, S. G. Stewart and M. Murakami, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 10903 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. I. Seeman, Chem. Rev., 1983, 83, 83 CrossRef CAS; For selected examples: (b) J. Halpern, Science, 1982, 217, 401 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) C. R. Landis and J. Halpern, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109, 1746 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. Chen and W. R. Roush, Tetrahedron, 2013, 69, 5468 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- The vinyl silane unit in homoallylic alcohols 5 can be used directly for a variety of subsequent transformations. For selected references, see: (a) T. A. Blumenkopf and L. E. Overman, Chem. Rev., 1986, 86, 857 CrossRef CAS; (b) I. Fleming, A. Barbero and D. Walter, Chem. Rev., 1997, 97, 2063 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. E. Denmark and J. H.-C. Liu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 2978 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) D. A. Evans and Y. Aye, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 11034 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) E. A. Ilardi, C. E. Stivala and A. Zakarian, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 1727 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) K. Aikawa, Y. Hioki and K. Mikami, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 13922 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. K. Stille and B. L. Groh, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109, 813 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) M. S. Ermolenko, Tetrahedron Lett., 1996, 37, 6711 CrossRef CAS; (b) L. C. Dias and C. d. C. S. Gonsalves, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2008, 350, 1017 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. Chinchilla and C. Nájera, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 5084 RSC; (b) E.-i. Negishi, M. Qian, F. Zeng, L. Anastasia and D. Babinski, Org. Lett., 2003, 5, 1597 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) J. S. Yadav and V. Rajender, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2010, 2148 CrossRef CAS.
- 1,3-Dienylsilanes with other substitution patterns did not proceed or proceeded with low conversions under the developed conditions.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c9sc02905b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |