Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleA vinyl silylsilylene and its activation of strong homo- and heteroatomic bonds†
Matthew M. D.
Roy
 ,
Michael J.
Ferguson
,
Michael J.
Ferguson
 ,
Robert
McDonald
,
Robert
McDonald
 ,
Yuqiao
Zhou
and
Eric
Rivard
,
Yuqiao
Zhou
and
Eric
Rivard
 *
*
Department of Chemistry, University of Alberta, 11227 Saskatchewan Drive, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2G2. E-mail: erivard@ualberta.ca
First published on 24th May 2019
Abstract
The facile synthesis of a rare two-coordinate acyclic silylene (R2Si:) that is stabilized using a bulky vinylic N-heterocyclic olefin ligand and the strongly σ-donating hypersilyl group [Si(SiMe3)3]− is reported. This vinyl-substituted silylene exhibits an excellent combination of prolonged thermal stability along with high reactivity towards small molecules. Despite being stable for months in solution, the reactivity of this new silylene is manifest in its ambient temperature activation of strong B–H, Si–Cl, C–O, P–P and C–H bonds.
Introduction
The activation and functionalization of small molecules such as H2, CO, CO2, P4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and even N2
1 and even N2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 by Earth-abundant main group elements usually relies on the isolation of highly reactive element centers. In order to be synthetically viable, a delicate balance of stability and reactivity must be achieved. Amongst p-block compounds, those of Group 14 in the +II oxidation state (tetrelenes) have shown significant promise with regard to bond activation and catalysis.3 Silylenes, (R2Si:) still remain rare relative to the other Group 14 tetrelenes, owing in part to the general instability of SiII compounds.4 While coordinatively saturated examples of silylenes (e.g. Cp*2Si; Cp* = η5-C5Me5) had been reported previously,5 West and coworkers prepared the first example of an unsaturated two-coordinate N-heterocyclic silylene.6 It was only in 2012 that the first examples of isolable two-coordinate acyclic silylenes were simultaneously published (I and II, Scheme 1);7 in stark contrast, their heavier R2E: congeners (E = Ge, Sn, Pb; R = anionic ligand) were first reported decades prior.8 While a few examples of room temperature stable acyclic silylenes are known,7,9 all have been stabilized by two heteroatom-based ligands. Herein, we utilize a bulky vinylic ligand [MeIPr
2 by Earth-abundant main group elements usually relies on the isolation of highly reactive element centers. In order to be synthetically viable, a delicate balance of stability and reactivity must be achieved. Amongst p-block compounds, those of Group 14 in the +II oxidation state (tetrelenes) have shown significant promise with regard to bond activation and catalysis.3 Silylenes, (R2Si:) still remain rare relative to the other Group 14 tetrelenes, owing in part to the general instability of SiII compounds.4 While coordinatively saturated examples of silylenes (e.g. Cp*2Si; Cp* = η5-C5Me5) had been reported previously,5 West and coworkers prepared the first example of an unsaturated two-coordinate N-heterocyclic silylene.6 It was only in 2012 that the first examples of isolable two-coordinate acyclic silylenes were simultaneously published (I and II, Scheme 1);7 in stark contrast, their heavier R2E: congeners (E = Ge, Sn, Pb; R = anionic ligand) were first reported decades prior.8 While a few examples of room temperature stable acyclic silylenes are known,7,9 all have been stabilized by two heteroatom-based ligands. Herein, we utilize a bulky vinylic ligand [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]−, (MeIPr = [(MeCNDipp)2C]; Dipp = 2,6-iPr2C6H3) to generate the first two-coordinate acyclic silylene stabilized by a carbon-based donor.10 Despite the remarkable thermal stability of the title complex (MeIPrCH)Si{Si(SiMe3)3}, this vinyl silylsilylene was able to undergo the formal oxidative addition of several strong organic and inorganic bonds, including the regioselective activation/functionalization of white phosphorus (P4) and the activation of a primary C–H bond at room temperature.
CH]−, (MeIPr = [(MeCNDipp)2C]; Dipp = 2,6-iPr2C6H3) to generate the first two-coordinate acyclic silylene stabilized by a carbon-based donor.10 Despite the remarkable thermal stability of the title complex (MeIPrCH)Si{Si(SiMe3)3}, this vinyl silylsilylene was able to undergo the formal oxidative addition of several strong organic and inorganic bonds, including the regioselective activation/functionalization of white phosphorus (P4) and the activation of a primary C–H bond at room temperature.
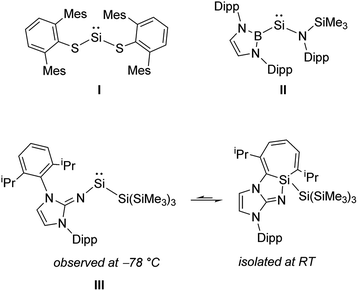 | ||
| Scheme 1 The first isolable two-coordinate acyclic silylenes (I and II) and the spectroscopically observed iminosilylene III. | ||
Results and discussion
This study relied upon the steric bulk and potential 4-electron (2σ, 2π) donating ability of the carbon-based anionic vinylic ligand [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]−,11 to gain access to a two-coordinate silylene. This ligand represents the deprotonated form of its neutral N-heterocyclic olefin (NHO)12 parent MeIPr
CH]−,11 to gain access to a two-coordinate silylene. This ligand represents the deprotonated form of its neutral N-heterocyclic olefin (NHO)12 parent MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2, and this vinylic ligand has been previously used in our group to isolate the first base-free divinylgermylene (MeIPrCH)2Ge.11
CH2, and this vinylic ligand has been previously used in our group to isolate the first base-free divinylgermylene (MeIPrCH)2Ge.11
The first step towards accessing a new organosilylene was to install the [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− ligand at silicon. This was achieved by the synthesis of the silane (MeIPrCH)SiBr3 (1) from mixing two equivalents of the olefin proligand MeIPr
CH]− ligand at silicon. This was achieved by the synthesis of the silane (MeIPrCH)SiBr3 (1) from mixing two equivalents of the olefin proligand MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 with SiBr4. After filtration from the flocculant [MeIPrCH3]Br precipitate, the target SiIV precursor 1 was isolated as an off-white, crystalline solid in a 53% yield (Scheme 2). Attempts to the prepare the divinyl silane (MeIPrCH)2SiBr2 by combining 1 with an additional two equivalents of MeIPr
CH2 with SiBr4. After filtration from the flocculant [MeIPrCH3]Br precipitate, the target SiIV precursor 1 was isolated as an off-white, crystalline solid in a 53% yield (Scheme 2). Attempts to the prepare the divinyl silane (MeIPrCH)2SiBr2 by combining 1 with an additional two equivalents of MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 or one equivalent of MeIPrCH(SiMe3)11 were unsuccessful. We then focused our synthetic studies on preparing a silylene directly from 1.
CH2 or one equivalent of MeIPrCH(SiMe3)11 were unsuccessful. We then focused our synthetic studies on preparing a silylene directly from 1.
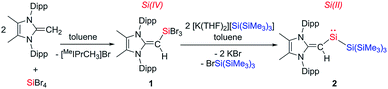 | ||
| Scheme 2 Formation of the tribromo-vinylsilane 1 and its subsequent reduction to the vinyl silylsilylene 2. | ||
Following recent reports of bulky silyl-substituted silylenes,5a,9a,c (MeIPrCH)SiBr3 (1) was combined with two equivalents of hypersilyl potassium [K(THF)2][Si(SiMe3)3] in toluene (Scheme 2). This resulted in the immediate formation of deep green slurry. 1H NMR spectroscopic analysis of the filtrate revealed quantitative conversion to a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of a new [MeIPr
1 mixture of a new [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− containing product and BrSi(SiMe3)3. The vinylic proton signal in the new product exhibited two-bond coupling satellites to Si (2JH–Si = 13.5 Hz), and its remarkably downfield-positioned chemical shift (δ 7.40 in C6D6) indicates significant transfer of electron density from the [MeIPr
CH]− containing product and BrSi(SiMe3)3. The vinylic proton signal in the new product exhibited two-bond coupling satellites to Si (2JH–Si = 13.5 Hz), and its remarkably downfield-positioned chemical shift (δ 7.40 in C6D6) indicates significant transfer of electron density from the [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− ligand to silicon. Additionally, the 29Si{1H} NMR spectrum displayed a signal at 432.9 ppm, which lies in the spectral range of known two-coordinate acyclic silylenes.9
CH]− ligand to silicon. Additionally, the 29Si{1H} NMR spectrum displayed a signal at 432.9 ppm, which lies in the spectral range of known two-coordinate acyclic silylenes.9
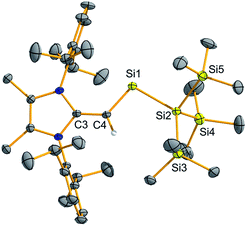
To confirm the formation of the two-coordinate silylene (MeIPrCH)Si{Si(SiMe3)3} (2), deep-green crystals suitable for X-ray crystallographic analysis were grown from Me3SiOSiMe3. The molecular structure of 2 (Fig. 1) is in good agreement with the abovementioned NMR results. Specifically, the vinylic C3–C4 bond in 2 [1.406(3) Å] is elongated relative to free NHO MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 [1.3489(18) Å],13 providing added evidence for the transfer of π-electron density to silicon. The C4–Si1–Si2 angle was found to be 101.59(7)°, in line with the presence of a high degree of s-character at the silicon-based lone pair. This angle implies that 2 should have a good balance of stability and reactivity. For example, the colorless dithiolato-supported silylene Si(SArMes)2 (I in Scheme 1) has an R–Si–R angle of 90.519(19)° indicating a relatively low-energy Si-based lone pair of pure s-character.7a While this molecule has not been reported to cleave strong organic bonds,14 acyclic silylenes with obtuse R–Si–R angles (and smaller HOMO–LUMO gaps) have been shown to activate small molecules such as H2, CO2, and NH3.7b,9
CH2 [1.3489(18) Å],13 providing added evidence for the transfer of π-electron density to silicon. The C4–Si1–Si2 angle was found to be 101.59(7)°, in line with the presence of a high degree of s-character at the silicon-based lone pair. This angle implies that 2 should have a good balance of stability and reactivity. For example, the colorless dithiolato-supported silylene Si(SArMes)2 (I in Scheme 1) has an R–Si–R angle of 90.519(19)° indicating a relatively low-energy Si-based lone pair of pure s-character.7a While this molecule has not been reported to cleave strong organic bonds,14 acyclic silylenes with obtuse R–Si–R angles (and smaller HOMO–LUMO gaps) have been shown to activate small molecules such as H2, CO2, and NH3.7b,9
(MeIPrCH)Si{Si(SiMe3)3} (2) is remarkably stable, with no NMR spectroscopic sign of decomposition noted after storage of a benzene solution at room temperature for two months (under N2 atmosphere). This observation contrasts the situation in Inoue and Rieger's imino silylsilylene (III, Scheme 1), which exists predominately in a 7-membered SiIV ring (silepin) form (via reversible ligand activation) at ambient temperature.9c Furthermore, our group's attempts to generate the bis-iminosilylene (IPrN)2Si: consistently afforded irreversible ligand activation products.15 Additionally, silylenes generated using hypersilyl potassium are often contaminated with the highly soluble BrSi(SiMe3)3 byproduct,9a,c however in our case pure 2 can be obtained in moderate yield (67%) by washing the crude residue with a minimal amount of cold (−30 °C) Me3SiOSiMe3.
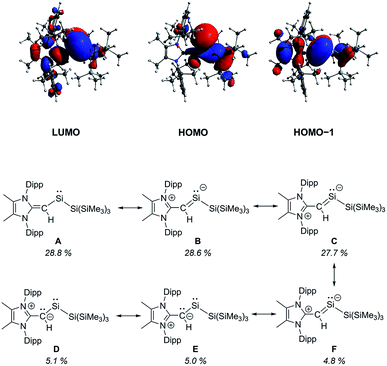
To gain further insight into the influence of the [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− ligand in 2, we conducted a series of computational (DFT) studies at the M06-2X/def2-TZVP level.16 The computed HOMO of 2 is predominately a silicon-based lone pair whereas the HOMO−1 consists of a C–Si π bond between the vinylic ligand and the silylene center (Fig. 2). The C–Si Wiberg Bond Index (WBI) was found to be 1.06 and the LUMO shows significant C–Si π* orbital character. Natural Resonance Theory (NRT) analysis further supports this bonding description, as three of the most relevant resonance structures (Fig. 2, structures B, C and F) contain a C–Si π bond with a combined 61.1% weighting of these structures. Together, these analyses demonstrate the stabilizing π-donation ability of the [MeIPr
CH]− ligand in 2, we conducted a series of computational (DFT) studies at the M06-2X/def2-TZVP level.16 The computed HOMO of 2 is predominately a silicon-based lone pair whereas the HOMO−1 consists of a C–Si π bond between the vinylic ligand and the silylene center (Fig. 2). The C–Si Wiberg Bond Index (WBI) was found to be 1.06 and the LUMO shows significant C–Si π* orbital character. Natural Resonance Theory (NRT) analysis further supports this bonding description, as three of the most relevant resonance structures (Fig. 2, structures B, C and F) contain a C–Si π bond with a combined 61.1% weighting of these structures. Together, these analyses demonstrate the stabilizing π-donation ability of the [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− ligand. Additionally, the computed natural charges show a highly polarized SiII–SiR3 bond (SiII: +0.54; SiR3: −0.51) which may enable interesting reactivity to transpire. As a result, we explored the interaction of 2 with small molecules in detail.
CH]− ligand. Additionally, the computed natural charges show a highly polarized SiII–SiR3 bond (SiII: +0.54; SiR3: −0.51) which may enable interesting reactivity to transpire. As a result, we explored the interaction of 2 with small molecules in detail.
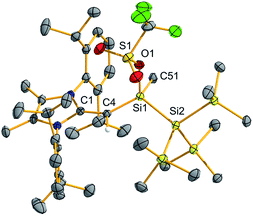
We began a reactivity study of 2 by combining this silylene with the carbon-based electrophile MeOTf (OTf = CF3SO3). As anticipated, the deep green color of 2 dissipated upon addition of MeOTf and NMR analysis revealed the formation of a single new product. X-ray crystallography identified this species as the new triflato-silane (MeIPrCH)Si(Me)OTf{Si(SiMe3)3} (3) (Scheme 3, Fig. 3). Compound 3 crystallizes in a distorted tetrahedral geometry, with a covalently bound -OTf unit in the solid state [Si1–O1 = 1.8258(10) Å] and in solution (19F{1H} NMR: δ −75.8 ppm).
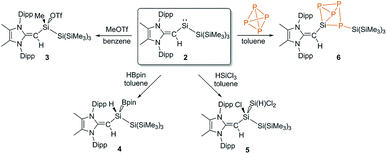 | ||
| Scheme 3 Oxidative addition of the substrates MeOTf (3), HBpin (4), HSiCl3 (5) and P4 (6) to the reactive silylene 2. | ||
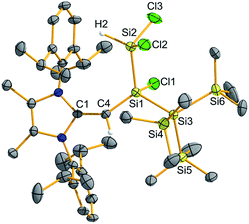
Silylene 2 was then combined with the widely used hydroborylation reagent pinacolborane (HBPin), which led to oxidative addition of an H–B bond at silicon to yield (MeIPrCH)Si(H)BPin{Si(SiMe3)3} (4) (Scheme 3). When 2 was reacted with trichlorosilane (HSiCl3), a new compound was soon observed with a singlet Si–H resonance in the 1H NMR spectrum (δ 3.61 ppm, 1JH–Si = 180.0 Hz). The lack of 3JHH coupling to the neighbouring vinylic hydrogen implied that oxidative addition of an Si–Cl bond had transpired in place of Si–H bond activation.17 Crystallographic analysis confirmed the formation of (MeIPrCH)SiCl(HSiCl2){Si(SiMe3)3} (5) (Fig. 4). Of note, the addition of HSiCl3 across a silylene (such as Cl2Si:) is a key step proposed in the chemical vapour deposition (CVD) of epitaxial silicon from trichlorosilane.18 The sterically congested nature of 5 is evident by its 1H and 13C{1H} NMR spectra which are very broad at room temperature but are resolved at +75 °C. The molecular structure of 5 (Fig. 4) shows an expected distorted tetrahedral geometry at Si1 [Si2–Si1–Si3: 109.81(9)°]. Interestingly, the located silane hydrogen atom was found to exhibit an SiH–π interaction in the solid state (H⋯Dippcentroid distance: 2.33 Å). Attempts to induce dehydrochlorination of 5 (to form a dichlorodisilene, RR′Si![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) SiCl2) using the strong Brønsted bases DABCO (DABCO = 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) or the N-heterocyclic carbene (MeCNMe)2C: were unsuccessful.19 In both cases, no reaction was observed, perhaps owing to steric protection of the Si–H bond.
SiCl2) using the strong Brønsted bases DABCO (DABCO = 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) or the N-heterocyclic carbene (MeCNMe)2C: were unsuccessful.19 In both cases, no reaction was observed, perhaps owing to steric protection of the Si–H bond.
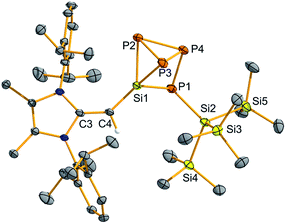
Encouraged by the activation of polarized heteroatomic bonds using 2, we decided to investigate whether silylene 2 would react with the non-polar bonds of white phosphorus (P4). While acyclic silylenes have not yet been shown to react with P4, several examples of cyclic silylenes reacting with P4 are known. These reactions are limited to the oxidative addition of a single P–P bond across a silicon center,20 and the controlled activation/functionalization of P4 by main group elements remains a difficult transformation.21 Upon mixing 2 and P4 for 20 minutes at room temperature, a pale orange solution was formed. 31P{1H} NMR analysis suggested that simple oxidative addition of a P–P had not occurred, as three distinct signals were observed (δ 120.0, −181.0, −316.7 ppm).16 X-ray crystallographic analysis revealed that a 1,2-migration of the hypersilyl group of 2 transpired in addition to P4 reduction (Scheme 3, Fig. 5) to yield (MeIPrCH)Si(P4){Si(SiMe3)3} (6). This transformation is likely facilitated by the steric bulk of 2 and the polarized nature of the SiII–Si(SiMe3)3 bond (vide supra). While the mechanism of this reaction likely involves first the oxidative addition of a P–P bond of P4 to silylene 2, followed by a 1,2-silyl migration, we did not observe any experimental evidence for this postulated oxidative addition intermediate.22 The observed activation/functionalization of P4 by 2 represents the cleavage of two P–P bonds and the regioselective formation of four new Si–P bonds. Remarkably, a search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) revealed that compound 6 represents an entirely new bonding motif for the P42− ligand.23 Notably, silylated phosphines and phosphides are valuable precursors to element phosphide nanomaterials24 and organophosphines25 and thus their preparation from elemental phosphorus continues to be of great importance.
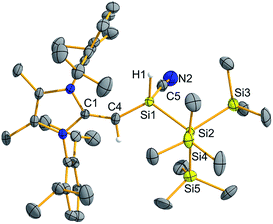
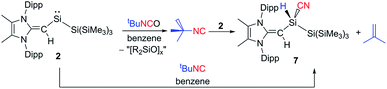
Following the remarkable report by Rieger, Inoue and coworkers of an isolable three-coordinate silanone (formed by oxidation of III in Scheme 1 with N2O)26 we wondered whether 2 would react in a similar manner. Surprisingly, exposure of a solution of 2 to an N2O atmosphere at −78 °C or room temperature afforded no reaction. Subsequently, 2 was combined with one equivalent of the potential oxygen-atom source tert-butyl isocyanate (tBuNCO) which yielded a mixture of products by 1H NMR spectroscopy, including several [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− containing species, unreacted tBuNCO and isobutylene. Extraction of the mixture with hexanes and crystallization afforded crystals of the silyl-cyanide (MeIPrCH)SiH(CN){Si(SiMe3)3} (7) in low (31%) yield (Fig. 6). Compound 7 is likely formed from the isocyanide (tBuNC) by-product generated after the initial oxidation of 2 with tBuNCO (Scheme 4). Thus far, we have been unable to isolate and identify the other products in the mixture, including the possible silanone by-product (MeIPrCH)Si(O){Si(SiMe3)3}. In order to give credence to the proposed mechanism, 2 was combined with one equivalent of tBuNC, which led to the quantitative formation of a 1
CH]− containing species, unreacted tBuNCO and isobutylene. Extraction of the mixture with hexanes and crystallization afforded crystals of the silyl-cyanide (MeIPrCH)SiH(CN){Si(SiMe3)3} (7) in low (31%) yield (Fig. 6). Compound 7 is likely formed from the isocyanide (tBuNC) by-product generated after the initial oxidation of 2 with tBuNCO (Scheme 4). Thus far, we have been unable to isolate and identify the other products in the mixture, including the possible silanone by-product (MeIPrCH)Si(O){Si(SiMe3)3}. In order to give credence to the proposed mechanism, 2 was combined with one equivalent of tBuNC, which led to the quantitative formation of a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of 7 and isobutylene (as determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy). This transformation represents a quantitative room temperature activation of a primary C–H bond by a silylene (R2Si:). Related transformations have been demonstrated previously with an acyclic germylene27 and a disilene,28 albeit at elevated temperatures.
1 mixture of 7 and isobutylene (as determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy). This transformation represents a quantitative room temperature activation of a primary C–H bond by a silylene (R2Si:). Related transformations have been demonstrated previously with an acyclic germylene27 and a disilene,28 albeit at elevated temperatures.
Conclusions
In this work, the synthesis of a thermally stable, two-coordinate acyclic silylene (MeIPrCH)Si{Si(SiMe3)3} was achieved, and is the first example of such a species supported by a carbon-based ligand. The stabilizing influence of [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− was evaluated experimentally and computationally. The high reactivity of this new silylene was demonstrated by its room temperature activations of strong homo- and heteroatomic bonds. Future work will target the synthesis of more nucleophilic sources of [MeIPr
CH]− was evaluated experimentally and computationally. The high reactivity of this new silylene was demonstrated by its room temperature activations of strong homo- and heteroatomic bonds. Future work will target the synthesis of more nucleophilic sources of [MeIPr![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH]− which may allow for the formation of a stable divinylsilylene and related reactive species for main group element-based catalysis.
CH]− which may allow for the formation of a stable divinylsilylene and related reactive species for main group element-based catalysis.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
E. R. thanks the NSERC of Canada for Discovery and CREATE grants, the Canada Foundation for Innovation, and the University of Alberta, Faculty of Science (Research Award) for funding. The computational studies in this work were made possible by the facilities of Compute/Calcul Canada (www.computecanada.ca). We thank Dr Paul Lummis for preliminary experimental investigations and Dr Emanuel Hupf for helpful discussions. Mr Mark Miskolzie is gratefully acknowledged for his assistance acquiring 29Si and variable temperature NMR spectra and Prof. Alex Brown for his helpful discussions relating to the computational work presented. We also thank Mr Samuel Baird for creating the TOC graphic. E. R. thanks the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation for fellowship.Notes and references
- For recent reviews and articles, see: (a) T. Chu and G. I. Nikonov, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 3608 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) P. P. Power, Nature, 2010, 463, 171 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) C. Weetman and S. Inoue, ChemCatChem, 2018, 10, 4213 CrossRef CAS; (d) R. L. Melen, Science, 2019, 363, 479 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) A. S. S. Wilson, M. S. Hill, M. F. Mahon, C. Dinoi and L. Maron, Science, 2017, 358, 1168 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) F.-G. Fontaine and E. Rochette, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 454 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) J. Hicks, P. Vasko, J. M. Goicoechea and S. Aldridge, Nature, 2018, 557, 92 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) Y. Wang, A. Kostenko, T. J. Hadlington, M.-P. Luecke, S. Yao and M. Driess, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 626 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M.-A. Légaré, G. Bélanger-Chabot, R. D. Dewhurst, E. Welz, I. Krummenacher, B. Engels and H. Braunschweig, Science, 2018, 359, 896 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) K. A. Miller, T. W. Watson, J. E. Bender, M. M. Banaszak Holl and J. W. Kampf, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 982 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y. Peng, B. D. Ellis, X. Wang and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 12268 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Peng, J.-D. Guo, B. D. Ellis, Z. Zhu, J. C. Fettinger, S. Nagase and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 16272 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) S. K. Mandal and H. W. Roesky, Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 45, 298 CrossRef PubMed; (e) K. Inomata, T. Watanabe, Y. Miyazaki and H. Tobita, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 11935 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) A. V. Protchenko, J. I. Bates, L. M. A. Saleh, M. P. Blake, A. D. Schwarz, E. L. Kolychev, A. L. Thompson, C. Jones, P. Mountford and S. Aldridge, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 4555 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) M. M. D. Roy, S. Fujimori, M. J. Ferguson, R. McDonald, N. Tokitoh and E. Rivard, Chem.–Eur. J., 2018, 24, 14392 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) T. J. Hadlington, M. Driess and C. Jones, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 4176 RSC.
- Y. Mizuhata, T. Sasamori and N. Tokitoh, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 3479 CrossRef CAS PubMed; M. Asay, C. Jones and M. Driess, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 354 CrossRef PubMed; E. Rivard, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 989 RSC.
- (a) P. Jutzi, U. Holtmann, D. Kanne, C. Krüger, R. Blom, R. Gleiter and I. Hyla-Kryspin, Chem. Ber., 1989, 122, 1629 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. H. Karsch, U. Keller, S. Gamper and G. Müller, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1990, 29, 295 CrossRef; (c) M. Kumar Bisai, V. S. V. S. V. S. N. Swamy, T. Das, K. Vanka, R. G. Gonnade and S. S. Sen, Inorg. Chem., 2019 DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b00418.
- M. Denk, R. Lennon, R. Hayashi, R. West, A. V. Belyakov, H. P. Verne, A. Haaland, M. Wagner and N. Metzler, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 2691 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) B. D. Rekken, T. M. Brown, J. C. Fettinger, H. M. Tuononen and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 6504 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. V. Protchenko, K. H. Birjkumar, D. Dange, A. D. Schwarz, D. Vidovic, C. Jones, N. Kaltsoyannis, P. Mountford and S. Aldridge, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 6500 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. S. Gynane, D. H. Harris, M. F. Lappert, P. P. Power, P. Rivière and M. Rivière-Baudet, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1977, 2004 RSC.
- (a) A. V. Protchenko, A. D. Schwarz, M. P. Blake, C. Jones, N. Kaltsoyannis, P. Mountford and S. Aldridge, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 568 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) T. J. Hadlington, J. A. B. Abdalla, R. Tirfoin, S. Aldridge and C. Jones, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 1717 RSC; (c) D. Wendel, A. Porzelt, F. A. D. Herz, D. Sakar, C. Jandl, S. Inoue and B. Rieger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 8134 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Y. K. Loh, L. Ying, M. Á. Fuentes, D. C. H. Do and S. Aldridge, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 4847 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A cyclic dialkylsilylene has been previously reported: M. Kira, S. Ishida, T. Iwamoto and C. Kabuto, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 9722 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) C. Hering-Junghans, P. Andreiuk, M. J. Ferguson, R. McDonald and E. Rivard, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 6272 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) For an example of a base-stabilized divinylgermylene, see: M. Walewska, J. Baumgartner and C. Marschner, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 276 RSC.
- For reviews on NHO ligands, see: (a) R. S. Ghadwal, Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 16081 RSC; (b) R. D. Crocker and T. V. Nguyen, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 2208 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. M. D. Roy and E. Rivard, Acc. Chem. Res., 2017, 50, 2017 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Powers, C. Hering-Junghans, R. McDonald, M. J. Ferguson and E. Rivard, Polyhedron, 2016, 108, 8 CrossRef CAS.
- Dithiolatosilylenes have been reported to reversibly bind ethylene: F. Lips, J. C. Fettinger, A. Mansikkamäki, H. M. Tuononen and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 634 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. W. Lui, C. Merten, M. J. Ferguson, R. McDonald, Y. Xu and E. Rivard, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 2040 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For full crystallographic, computational, and experimental details see the ESI.† CCDC 1901003 to 1901008 contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this manuscript.†.
- A similar reaction has been previously reported for a cyclic silylene, however a mixture of two products was observed: Y. Xiong, S. Yao and M. Driess, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 1927 CrossRef CAS.
- M. T. Swihart and R. W. Carr, J. Phys. Chem. A, 1998, 102, 1542 CrossRef CAS.
- Hydrodechlorination of chlorosilanes using strong neutral bases is known. For example: R. S. Ghadwal, H. W. Roesky, S. Merkel, J. Henn and D. Stalke, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 5683 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Driess, A. D. Fanta, D. R. Powell and R. West, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1989, 28, 1038 CrossRef; (b) Y. Xiong, S. Yao, M. Brym and M. Driess, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 4511 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. S. Sen, S. Khan, H. W. Roesky, D. Kratzert, K. Meindl, J. Henn, D. Stalke, J.-P. Demers and A. Lange, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 2322 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For selected reviews of P4 activation by main group elements, see: (a) M. Scheer, G. Balázs and A. Seitz, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 4236 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Khan, S. S. Sen and H. W. Roesky, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 2169 RSC; (c) J. E. Borger, A. W. Ehlers, J. C. Slootweg and K. Lammertsma, Chem.–Eur. J., 2017, 23, 11738 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- In an attempt to observe this potential intermediate, the reaction of 2 + P4 was monitored by 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopy in toluene-d8. At −80 °C, we observed only 6 + unreacted P4. At −60 °C and above, several new signals were observed, however none of the signals clearly correspond to a P4-containing intermediate. In contrast, when the reaction of 2 + P4 was monitored by 31P{1H} NMR at room temperature, clean conversion to 6 was observed. This divergent reactivity may be due to significantly different solubilities of P4 and 2 at low temperature, thus altering the effective stoichiometry in solution.
- The activation of P4 by H2Si: has been studied computationally. Interestingly, none of the located minima on the potential energy surface correspond to compound 6: R. Damrauer and S. E. Pusede, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 1289 CrossRef CAS.
- For example: D. C. Gary and B. M. Cossairt, Chem. Mater., 2013, 25, 2463 CrossRef CAS.
- M. B. Geeson and C. C. Cummins, Science, 2018, 359, 1383 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Wendel, D. Reiter, A. Porzelt, P. J. Altmann, S. Inoue and B. Rieger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 17193 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. D. Brown, P. Vasko, J. C. Fettinger, H. M. Tuononen and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 4045 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Takeda, T. Kajiwara, H. Suzuki, R. Okazaki and N. Tokitoh, Chem.–Eur. J., 2003, 9, 3530 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Full details relating to experimental, crystallographic and computational procedures. CCDC 1901003–1901008. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c9sc01192g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |