Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleDivergent synthesis of a thiolate-based α-hydroxytropolone library with a dynamic bioactivity profile†
Nana B. Agyemang ab,
Cassandra R. Kuklac,
Tiffany C. Edwardsc,
Qilan Lic,
Madison K. Langend,
Alexandra Schaald,
Abaigeal D. Fransonc,
Andreu Gazquez Casalsc,
Katherine A. Donaldc,
Alice J. Yuc,
Maureen J. Donlin
ab,
Cassandra R. Kuklac,
Tiffany C. Edwardsc,
Qilan Lic,
Madison K. Langend,
Alexandra Schaald,
Abaigeal D. Fransonc,
Andreu Gazquez Casalsc,
Katherine A. Donaldc,
Alice J. Yuc,
Maureen J. Donlin d,
Lynda A. Morrison
d,
Lynda A. Morrison ce,
John E. Tavis
ce,
John E. Tavis c and
Ryan P. Murelli
c and
Ryan P. Murelli *ab
*ab
aDepartment of Chemistry, Brooklyn College, The City University of New York, Brooklyn, New York 11210, USA. E-mail: rpmurelli@brooklyn.cuny.edu
bPhD Program in Chemistry, The Graduate Center of The City University of New York, New York, New York 10016, USA
cDepartment of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri 63104, USA
dEdward A. Doisy Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri 63104, USA
eDepartment of Internal Medicine, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri 63110, USA
First published on 23rd October 2019
Abstract
Here we describe a rapid and divergent synthetic route toward structurally novel αHTs functionalized with either one or two thioether or sulfonyl appendages. Evaluation of this library against hepatitis B and herpes simplex virus, as well as the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans, revealed complementary biological profiles and new lead compounds with sub-micromolar activities against each pathogen and high selectivities when compared to mammalian cell lines.
Introduction
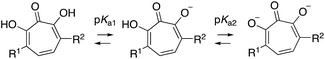
α-Hydroxytropolone (αHT, 1, Fig. 1A) is a highly oxygenated troponoid with 3 contiguous oxygen atoms that give it the capacity to coordinate two metals in the active sites of many dinuclear metalloenzymes.1 As such, it has been of interest as a metal-binding fragment in a broad range of drug-development pursuits.2 One of the major obstacles historically associated with exploiting αHT in drug development, however, has been a scarcity of methods capable of producing functionalized variants.3 As a result, most of what is known about the activity of αHTs has stemmed from natural products, and in particular β-thujaplicinol (2),4 a simple natural product variant with a fairly promiscuous activity profile (e.g., Fig. 1B).5 In addition, the few synthetic chemistry-driven structure–function studies that have been conducted have generally focused on highly structurally homologous molecules.6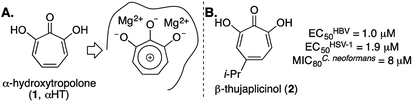 | ||
| Fig. 1 α-Hydroxytropolone (αHT) overview. (A) αHT and potential mode of inhibition of dinuclear metalloenzymes. (B) αHT natural product β-thujaplicinol, and previously published data against HBV, HSV-1, and C. neoformans.5 | ||
Driven by this need, over the last several years our lab has been studying an oxidopyrylium cycloaddition/ring-opening route to generate a diverse range of αHTs (Scheme 1).7 This strategy is highly effective at installing a variety of functionalities at position 4 (inset, Scheme 1). However, installing functionality at the 3 position, adjacent to the metal-binding oxygens, is more laborious using this strategy,8 and it is not clear at present how the method could install functionality at both the 3- and 6- positions. Given this proximity, it would be expected that molecules with appendages at the 3 and/or 6 positions would more readily engage protein targets either positively or negatively, and as a result have a more dynamic biological activity profile. Thus, strategies that can conveniently install groups at these positions would be complementary to existing synthetic strategies, and as such would be valuable in the continued development of αHT-based therapeutics.
 | ||
| Scheme 1 Oxidopyrylium cycloaddition/ring-opening strategy for αHT synthesis. Inset is a structure representative of a high percentage of current library made through this approach. | ||
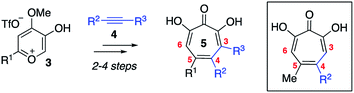
Here we describe the divergent synthesis and biological evaluation of a library of new αHTs that have thioether and sulfonyl appendages at one or both of these positions (Scheme 2B). The thioether-appended αHTs are synthesized through a rapid halogenation/thiolate addition sequence and are then oxidized to generate an additional set of sulfonyl-containing αHTs. Profiling the library against three common pathogenic microbes, hepatitis B virus (HBV), herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) and Cryptococcus neoformans (C. neoformans), establishes the dynamic and complementary bioactivity profile that exists among accessible molecules, and provides new lead scaffolds with sub-micromolar activity that should serve as new starting points for drug-development pursuits.
 | ||
| Scheme 2 Halogenation/functionalization approaches to substituted tropolones. (A) Halogenation/cross-coupling strategy to functionalize 3,7-dihydroxytropolones.9 (B) Halogenation/thiolate addition/oxidation strategy described herein. | ||
Results and discussion
Synthesis
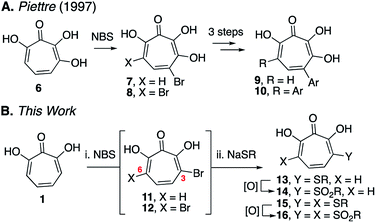
Our synthetic strategy was largely inspired by a halogenation/cross-coupling sequence exploited by Piettre and co-workers in the synthesis of a series of mono- and bis-arylated 3,7-dihydroxytropolones (Scheme 2A).9 Given the value of the strategy in accessing one or both sites adjacent to the metal-binding oxygen triad, we became curious if a similar route might be useful in generating αHTs functionalized at similar positions. Rather than aryl–aryl cross-coupling chemistry, however, we decided to investigate thiolate addition chemistry. Thiolate addition chemistry had been established for halo tropolone functionalization,10 and the ability to oxidize to the sulfonyl would provide an additional αHT analogues with different electronic properties. Furthermore, given our desire to keep the synthesis as simple as possible, we also wanted to avoid the late-stage tropolone protection used in the Piettre studies. In this regard, it was known that thiolates could react as nucleophiles in the presence of unprotected αHTs.6bαHT 1 was thus synthesized on multigram scale in 4 steps from tropolone employing a method closely derived from that developed by Takeshita.11 Piettre had previously described in-depth the challenges of 3,7-dihydroxytropolone monohalogenation for production of 7 due to the high bis-halogenated product 8, and in order to maximize production of 7 used slow addition of N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) and only took the reaction to partial conversion.9 We decided instead to embrace the combinatorial chemistry-type benefits this non-selective halogenation provided. After exploration of various halogenation conditions, we found that refluxing a solution of 1 and 2 equivalents of N-bromosuccinimide in benzene over a period of 24 h yielded a mixture of 7 and 8 in a roughly equimolar ratio. Rather than purify at this step, upon evaporation of the benzene, we immediately added sodium thiolates in DMSO to the reaction vessel and heated the reaction mixture to 80 °C for 24 h. Upon cooling, the DMSO solution was loaded directly onto a C18 reverse phase column (Biotage Isolera Prime, C18 SNAP) and chromatographed to isolate pure mono- and bis-thioether hydroxytropolones, 13a–h and 15a–h. These αHTs were individually converted into mono- and bis-sulfones 14a–h and 16a–h following oxidation with mCPBA.12 Thus, we found that from αHT 1 and single thiol or thiolate, we could readily access as many as 4 unique αHTs in only 3 steps.
This chemical sequence was performed with 8 different sodium thiolates, which included aliphatic (entry 1–4), aromatic (entries 5–7), and a benzyl thiolate (entry 8) (Scheme 3). All 16 monosubstituted thioether (13a–h)- and sulfonyl (14a–h)-containing αHTs were successfully generated. On the other hand, only 9 of the 16 disubstituted αHTs were successfully made and purified. One of the limitations to the procedure was the addition of the aromatic thiolates, which did not provide the corresponding bis thiolates cleanly (15e–g), even when attempting to make them from purified dibrominated αHT 12. It is unclear why these specific molecules were problematic, but our inability to generate them meant that we were also unable to access the bis sulfonyl compounds of this series (16e–g). One other molecule that we were unable to generate was 16a. Nonetheless, even without having access to this subset of molecules, we were able to rapidly generate 25 unique αHTs from 1 and 8 thiolates.
 | ||
| Scheme 3 Synthesis of thioether and sulfonyl αHTs. aIsolated yields following C18-capped silica gel chromatography. bThiolates made and used in situ from sodium hydride and the corresponding thiol. See ESI† for detail. | ||
Biological studies
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cases of which result in visual impairment or blindness.17 Although less frequent, when HSV-1 spreads to the central nervous system, it can cause life-threatening herpetic encephalitis in adults and in babies infected during birth.18 Current anti-HSV therapy employs nucleos(t)ide analogs which are incompletely effective18b and lead to drug-resistance.18c New treatment options for HSV-1 infections are thus of high interest.
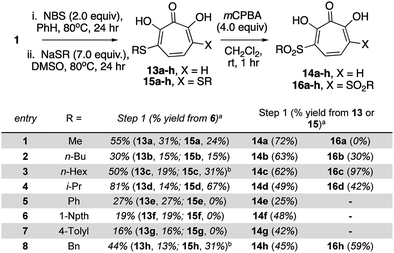
000 cases of which result in visual impairment or blindness.17 Although less frequent, when HSV-1 spreads to the central nervous system, it can cause life-threatening herpetic encephalitis in adults and in babies infected during birth.18 Current anti-HSV therapy employs nucleos(t)ide analogs which are incompletely effective18b and lead to drug-resistance.18c New treatment options for HSV-1 infections are thus of high interest.αHTs have been identified as potent inhibitors of the virus, with measured effective concentrations for 50% viral replication suppression (EC50) as low as 50 nM (Fig. 3).8 While studies are ongoing to establish the likely mechanism of action, certain αHTs are known to inhibit at least two HSV-1 nucleases, UL1519 and UL12,20 and also act synergistically with current antivirals.14 αHTs also have demonstrable activity against other herpesviruses including human cytomegalovirus5b and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus,21 as well as several animal herpesviruses.22 For all these reasons, the continued development of αHTs as antiviral agents against HSV-1 is warranted.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 Representative examples of potent anti-HSV-1 αHTs previously tested.8,23. | ||
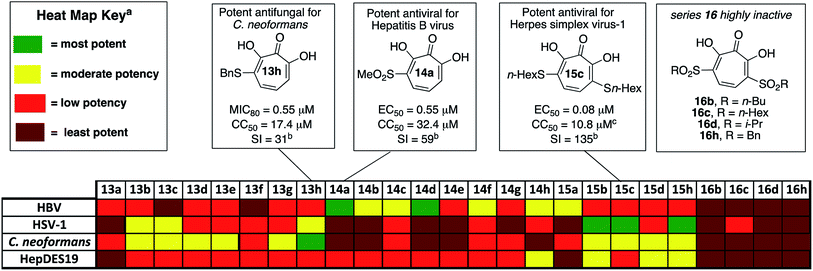
The 25 thiolate-based αHTs were thus screened in plaque reduction assays at concentrations of 5 μM, 1 μM, and 0.33 μM. From this screen, 6 molecules were found to suppress viral replication by at least 10-fold at a concentration of 1 μM (See Fig. 2 and the ESI†). These molecules each share a common set of 3 thioether-based appendages, n-butyl, n-hexyl and benzyl thioether. Of these molecules, the 3 bis-thioether compounds of the series (15b/c/h) maintained significant inhibitory activity at 0.33 μM. Additional experiments with these 6 molecules were carried out to obtain more quantitative EC50 values (Table 1). Consistent with the screening findings, the bis-thioether molecules (EC50 = 0.08–0.26 μM) were more potent than their corresponding mono-thioether congeners (EC50 = 0.59–1 μM). While 15c and 15h were among the more cytotoxic molecules when tested against HepDES19 cells (CC50 = ∼8 μM), they showed no cytotoxicity at up to 100 μM against Vero cells, which were the host cell line for the anti-HSV-1 assays. Thus, 15c and 15d, have cell-based activity profiles on par with the most potent anti-HSV-1 αHTs developed to date, and as such reveal an alternative starting point for further optimization studies.
| Cmpd | EC50 ± SEa (μM) | CC50 ± SEa (μM) | clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Pb Pb |
|---|---|---|---|
a EC50 and CC50 values calculated from the average of 3 runs ± standard error.b clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P values calculated in monoanionic state using ChemDraw Professional, version 15.0. P values calculated in monoanionic state using ChemDraw Professional, version 15.0. |
|||
| 13b | 1.01 ± 0.32 | >100 | −0.93 |
| 13c | 0.93 ± 0.08 | >100 | 0.13 |
| 13h | 0.59 ± 0.06 | >100 | −0.95 |
| 15b | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 87.2 ± 4.6 | 1.23 |
| 15c | 0.08 ± 0.00 | >100 | 3.35 |
| 15h | 0.08 ± 0.02 | >100 | 1.19 |
In addition to the new leads that emerged, the totality of the structure–function studies also provided additional insight that could be useful in guiding further optimization. Recently, we disclosed an αHT-based structure–activity relationship (SAR) based upon oxidopyrylium cycloaddition/ring-opening approach to the molecules that found that lipophilicity (as determined in the monoanionic state by clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P) correlates highly with potent anti-HSV activity, with some secondary trends illustrating the potential importance of side-chain rigidity.23 The SAR of the thiolate-based αHT library revealed some trends consistent with this activity. Compounds 15b/c/h had the highest clog
P) correlates highly with potent anti-HSV activity, with some secondary trends illustrating the potential importance of side-chain rigidity.23 The SAR of the thiolate-based αHT library revealed some trends consistent with this activity. Compounds 15b/c/h had the highest clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P values of the thiolate-based library, and were the only three compounds with clog
P values of the thiolate-based library, and were the only three compounds with clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P values in the monoanionic state exceeding 1. 15c was by far the most lipophilic molecule (clog
P values in the monoanionic state exceeding 1. 15c was by far the most lipophilic molecule (clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P = 3.35, Table 1), and was one of the two most potent molecules, along with 15h. 15h had comparable clog
P = 3.35, Table 1), and was one of the two most potent molecules, along with 15h. 15h had comparable clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P value to 15b, but was 4 times more potent. This could be the result of the rigidity of the aromatic appendage, which further restricts the number of rotatable bonds when compared to 15b. Similar increases in potency can be observed in the mono-thioether series (13h vs. 13b). It is worth noting, however, that 1-napthyl-containing thioether, 13f, is both more lipophilic (clog
P value to 15b, but was 4 times more potent. This could be the result of the rigidity of the aromatic appendage, which further restricts the number of rotatable bonds when compared to 15b. Similar increases in potency can be observed in the mono-thioether series (13h vs. 13b). It is worth noting, however, that 1-napthyl-containing thioether, 13f, is both more lipophilic (clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P = 0.44) and more rigid than 13h, and yet is inactive at 1 μM. One hypothesis to explain this discrepancy is that some flexibility is needed to achieve proper contact with the target enzyme. Structure–function studies on this new library provide additional trends that appear to confirm the importance of both lipophilicity and rigidity in the design of more potent αHT-based anti-HSV-1 agents. This information should help guide future optimization studies on the molecules.
P = 0.44) and more rigid than 13h, and yet is inactive at 1 μM. One hypothesis to explain this discrepancy is that some flexibility is needed to achieve proper contact with the target enzyme. Structure–function studies on this new library provide additional trends that appear to confirm the importance of both lipophilicity and rigidity in the design of more potent αHT-based anti-HSV-1 agents. This information should help guide future optimization studies on the molecules.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 new cases of Cryptococcal meningitis and 140
000 new cases of Cryptococcal meningitis and 140![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 Cryptococcal meningitis-related deaths per year. Cryptococcal infections are also common in solid organ transplant patients, with estimates of 3% of the population developing fungal infections within the first year, and patients remaining at high risk of infection for 5 years.25 When left untreated, 1 year mortality rates from Cryptococcal meningitis range from 30% to 100%, depending on the region. While antifungal agents such as amphotericin B and fluconazole can be effective, the prognosis for survival among treated patients remains poor (20% to 70%, depending on region). Furthermore, these drugs have significant toxicity issues associated with them. Thus, the development of new classes of antifungal agents targeting C. neoformans is of high interest.
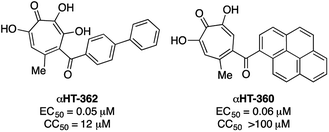
000 Cryptococcal meningitis-related deaths per year. Cryptococcal infections are also common in solid organ transplant patients, with estimates of 3% of the population developing fungal infections within the first year, and patients remaining at high risk of infection for 5 years.25 When left untreated, 1 year mortality rates from Cryptococcal meningitis range from 30% to 100%, depending on the region. While antifungal agents such as amphotericin B and fluconazole can be effective, the prognosis for survival among treated patients remains poor (20% to 70%, depending on region). Furthermore, these drugs have significant toxicity issues associated with them. Thus, the development of new classes of antifungal agents targeting C. neoformans is of high interest.A recent survey of troponoids against C. neoformans revealed that αHT 1 had modest inhibition on the growth of C. neoformans, with an 80% minimum growth inhibition concentration (MIC80) of 24 μM.5c In addition to this molecule, 35 substituted αHTs were also evaluated, but none of these molecules was substantially more potent (Fig. 4 and Fig. 1). By contrast, when the 25-membered thiolate-based αHT library was tested for its ability to inhibit C. neoformans growth, ten different molecules had MIC80 values below 10 μM (Table 2 and Fig. 2). This library of potent molecules was specific to the thioether series (13 and 15) and included all but the methyl thiolate-based molecules 13a and 15a, and naphthyl thiolate-containing αHT 13f. Given that 13a had a MIC80 value equal to 1, it appears that the sulfur portion of the appendage may play very little role in these activity increases. The most potent molecule of the series contained a single benzylthioether (13h, MIC80 = 0.55 μM), and this molecule was 50 times more potent than αHT 1. The presence of a second thioether (15h, MIC80 = 7 μM), or replacement of the thioether with the analogous sulfone (14h, MIC80 = 50 μM) was deleterious to the activity. 13h had relatively moderate cytotoxicity against HepDES19 cells (CC50 = 17 μM), giving the molecule a selectivity index over 30. This value was over 6 times greater than any of the synthetic αHTs previously tested.5c Thus, 13h represents a substantial breakthrough for C. neoformans-targeting αHT-based antifungals. Furthermore, the structure–function data and synthetic strategy presented provide knowledge and opportunities that should be valuable for additional optimization studies.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Previously described αHTs with C. neoformans antifungal activity.5c | ||
| C. neoformans growth inhibition (MIC80) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13a–h | 14a–h | 15a–h | 16a–h | |
| R = Me | 13a (28 μM) | 14a (50 μM) | 15a (38 μM) | — |
| R = n-Bu | 13b (1 μM) | 14b (50 μM) | 15b (2.3 μM) | 16b (100 μM) |
| R = n-Hex | 13c (1.7 μM) | 14c (14 μM) | 15c (7 μM) | 16c (50 μM) |
| R = i-Pr | 13d (2.6 μM) | 14d (50 μM) | 15d (1.5 μM) | 16d (100 μM) |
| R = Ph | 13e (1.5 μM) | 14e (50 μM) | — | — |
| R = 1-Npth | 13f (21 μM) | 14f (38 μM) | — | — |
| R = 4-tolyl | 13g (1.7 μM) | 14g (38 μM) | — | — |
| R = Bn | 13h (0.55 μM) | 14h (50 μM) | 15h (7 μM) | 16h (73 μM) |
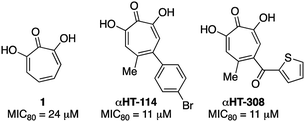
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 deaths annually.26 While the HBV vaccine is renowned for its success at curbing new hepatitis B cases, nearly 300 million people remain chronically infected worldwide. For these individuals, who have a 20–30% chance of developing cirrhosis and/or liver cancer due to HBV, current therapies based on interferon α or nucleos(t)ide analogs reduce death from hepatocellular carcinoma by only 2–4 fold5c and there is no cure. Thus, a major goal is to establish treatments that can yield durable elimination of viremia and halt disease progression following a limited-duration treatment regimen (a “functional cure”).27 As part of this effort, many research labs are trying to identify novel hepatitis B antivirals that profoundly suppress viral replication by attacking viral functions not targeted by the current drugs,28 probably through combination therapy with currently available antivirals.29 αHTs have been identified as potent anti-HBV agents, and αHT 1 has an EC50 of 1.7 μM, and no cytotoxicity against HepDES19 cells at up to 100 μM.13 Several synthetic derivatives have been identified with nearly 5-fold potency increases over 1, including compound αHT-110 (Fig. 5), which also suppresses HBV viremia in an animal model.30 We hypothesized that electron-withdrawing groups on the αHT could improve potency by stabilizing a dianionic state that may exist when the αHT is bound to the target enzyme, which is believed to be the dinuclear metalloenzyme HBV ribonuclease H (RNaseH).31 Thus, the thiolate-based library provided us with an opportunity to probe this structure–function activity relationship in more detail.
000 deaths annually.26 While the HBV vaccine is renowned for its success at curbing new hepatitis B cases, nearly 300 million people remain chronically infected worldwide. For these individuals, who have a 20–30% chance of developing cirrhosis and/or liver cancer due to HBV, current therapies based on interferon α or nucleos(t)ide analogs reduce death from hepatocellular carcinoma by only 2–4 fold5c and there is no cure. Thus, a major goal is to establish treatments that can yield durable elimination of viremia and halt disease progression following a limited-duration treatment regimen (a “functional cure”).27 As part of this effort, many research labs are trying to identify novel hepatitis B antivirals that profoundly suppress viral replication by attacking viral functions not targeted by the current drugs,28 probably through combination therapy with currently available antivirals.29 αHTs have been identified as potent anti-HBV agents, and αHT 1 has an EC50 of 1.7 μM, and no cytotoxicity against HepDES19 cells at up to 100 μM.13 Several synthetic derivatives have been identified with nearly 5-fold potency increases over 1, including compound αHT-110 (Fig. 5), which also suppresses HBV viremia in an animal model.30 We hypothesized that electron-withdrawing groups on the αHT could improve potency by stabilizing a dianionic state that may exist when the αHT is bound to the target enzyme, which is believed to be the dinuclear metalloenzyme HBV ribonuclease H (RNaseH).31 Thus, the thiolate-based library provided us with an opportunity to probe this structure–function activity relationship in more detail.
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Representative examples of previously described anti-HBV αHTs. (EC50) along with cytotoxicity against HepDES19 cells (CC50).13 | ||
Of the 25 thiolate-based αHTs, most of the molecules (23/25) had activity far less than 1 (Table 3). The two with improved activity were the two mono-sulfone-containing αHTs with the smallest appendages, 14a and 14d, and these were roughly 2-fold more potent than 1 (EC50 = 0.55 μM and 0.79 μM, respectively, Table 3). Unlike 1 and some of the top leads, these molecules had moderate cytotoxicity against HepDES19 cells (CC50 = 32 μM and 20 μM, respectively), but their selectivity indexes for HBV compared to the host cell line remained strong (59 and 25, respectively). Given our prior SAR suggesting that improved activity could be achievable by adding more electron-withdrawing capabilities,13b we had expected that the bis-sulfonyl series (16a–h) would be the most potent series tested. However, these molecules were all inactive. Given that the bis-thioether series (15a–h) were generally more active than the mono-thioether series (13a–h), it was initially suspected that the rapid drop in activity may be the result of electronic or cell-permeability differences rather than sterics. Compound 16d has a highly negative clog![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P value in the monoionic state (see Table 4), and it is possible that the electron-withdrawing appendages may increase the acidity of the molecules to the point that it would exist primarily in a dianionic state at physiological pH,32 lowering its permeability even further. This may also help explain the lack of activity of series 16 in all other cell types tested herein.
P value in the monoionic state (see Table 4), and it is possible that the electron-withdrawing appendages may increase the acidity of the molecules to the point that it would exist primarily in a dianionic state at physiological pH,32 lowering its permeability even further. This may also help explain the lack of activity of series 16 in all other cell types tested herein.
| 13a–h | 14a–h | 15a–h | 16a–h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R = Me | 13a (14.3 μM) | 14a (0.55 μM) | 15a (8.6 μM) | — |
| R = n-Bu | 13b (47 μM) | 14b (1.9 μM) | 15b (12 μM) | 16b (>50 μM) |
| R = n-Hex | 13c (50 μM) | 14c (6.6 μM) | 15c (11 μM) | 16c (50 μM) |
| R = i-Pr | 13d (31 μM) | 14d (0.79 μM) | 15d (12.7 μM) | 16d (>50 μM) |
| R = Ph | 13e (47 μM) | 14e (11.3 μM) | — | — |
| R = 1-Npth | 13f (>50 μM) | 14f (5.9 μM) | — | — |
| R = 4-tolyl | 13g (17 μM) | 14g (49 μM) | — | — |
| R = Bn | 13h (25 μM) | 14h (2.8 μM) | 15h (11 μM) | 16h (>50 μM) |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P values, as determined with ChemDraw Professional 15.0 in the monoanionic state
P values, as determined with ChemDraw Professional 15.0 in the monoanionic state
Thus, we became interested in assessing how a series of αHTs (13d–16d) might behave in biochemical assays where cell-permeability would not influence activity. It was postulated that if 16d was highly active biochemically, this would support the hypothesis that the lack of activity was due to low cell permeability. As stated earlier, the cell-based HBV antiviral activity of αHT is believed to be the result of RNaseH inhibition, which is supported by the presence of an RNaseH-deficient phenotype in cells treated with ribonuclease H inhibitors such as those tested here.5a An HBV RNaseH enzyme inhibition assay is available, although it is often the case that potent antiviral activity does not correlate well with enzymatic inhibition, which may be the result of the recombinant RNaseH protein being only part of the larger HBV polymerase protein.33 Thus, in addition to evaluating HBV RNaseH activity, we also tested the molecules for inhibition of human RNaseH1 and E. Coli RNaseH to more broadly evaluate the trend of RNaseH inhibition in relationship to molecule class. When the series of molecules was tested against these enzymes, however, we found that 16d was the least active against the entire series. Thus, we cannot conclude that the lack of activity of series 16 is due to a lack of cell permeability.
Conclusions
A divergent synthetic strategy is described that provides rapid access to a library of 25 functionalized αHTs from the parent αHT 1 and 8 thiolates. Profiling this library against three human pathogens (HBV, HSV and C. neoformans), as well as a human hepatoblastoma (HepDES19) revealed a dynamic activity profile, and unique new leads with sub-micromolar activity for each of the pathogens. These studies represent a new synthetic strategy to identify novel opportunities for developing αHTs as drug fragments, as well as structure–function insight to help guide them.Conflicts of interest
MJD, LAM, JET, and RPM are co-inventors on a patent describing αHTs as drug leads for the three diseases described herein.Author contributions
MJD, NBA and RPM synthesized and characterized library of molecules. CRK, RCE, QL, and JET obtained hepatitis B antiviral and HepDES19 cytotoxicity data. MKL, AS, and MJD obtained C. neoformans antifungal data. ADF, AGC, KAD, AJY, and LAM obtained herpes simplex virus-1 antiviral and Vero cytotoxicity data. RPM wrote manuscript, with primary input and assistance from NBA, MJD, LAM, and JET. Vero cells were a gift from Dr David Knipe (Harvard University), HepDES19 Cells were a gift from Dr Haitao Guo (Indiana University), and C. neoformans wild-type KN99α was a gift from Dr Jennifer Lodge (Washington University).Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health in the form of research grants awarded to RPM (SC1GM111158) and JET (R01AI122669). LAM appreciates support from the Pershing Trust. MJD received support from the Saint Louis University Presidential Research Fund. We thank Elena Lomonosova and Austin O'Dea for technical assistance.Notes and references
- C. Meck, M. P. D' Erasmo, D. R. Hirsch and R. P. Murelli, The biology and synthesis of α-hydroxytropolones, MedChemComm, 2014, 5, 842–852 RSC.
- For a few lead examples, see: (a) S. R. Piettre, A. Ganzhorn, J. Hoflack, K. Islam and J. M. Hornsperger, α-Hydroxytropolones: a new class of potent inhibitors of inositol monophosphatase and other bimetallic enzymes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 3201–3204 CrossRef CAS; (b) N. E. Allen, W. E. Alborn Jr, J. N. Hobbs Jr and J. H. A Kirst, 7-Hydroxytropolones: an inhibitor of aminoglycoside 2′′-O-adenyltransferase, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1982, 22, 824–831 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. R. Budihas, I. Gorshkova, S. Gaidamakov, A. Wamiru, M. K. Bona, M. A. Parniak, R. J. Crouch, J. B. McMahon, J. A. Beutler and S. F. J. Le Grice, Selective inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H activity by hydroxylated tropolones, Nucleic Acids Res., 2005, 33, 1249–1256 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) M. G. Banwell and M. P. Collis, The palladium-mediated cross-coupling of bromotropolones with organostannanes; application to concise syntheses of β-dolabrin, β-thujaplicin, 7-methoxy-4-isopropyltropolones, and β-thujaplicinol, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1991, 1343–1345 RSC; (b) J. Zinser, S. Henkel and B. Fohlisch, A novel synthesis of 2-alkoxy-3-hydroxytropones and 2,7-dihydroxytropones from dialkoxy- 8-oxabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-6-en-3-ones, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2004, 1344–1346 CrossRef; (c) T. Yamatani, M. Yasunami and K. Takase, Dehydrotropolones: a benzyne-type Intermediate in the reaction of halotropolones with alkoxides, Tetrahedron Lett., 1970, 11, 1752–1758 CrossRef.
- A. B. Anderson and J. Gripenberg, Antibiotic substances from the heart wood of Thuja plicata D. Don, Acta Chem. Scand., 1948, 2, 644–650 CrossRef CAS.
- For HBV, see: (a) Y. Hu, X. Cheng, F. Cao, A. Huang and J. E. Tavis, β-Thujaplicinol inhibits hepatitis B virus replication by blocking the viral ribonuclease H activity, Antivir. Res., 2013, 99, 221–229 CrossRef CAS . For HSV-1, see:; (b) J. E. Tavis, H. Wang, A. E. Tollefson, B. Ying, M. Korom, X. Cheng, F. Cao, K. L. Davis, W. S. M. Wold and L. A. Morrison, Inhibitors of nucleotidyltransferase superfamily enzymes suppress herpes simplex virus replication, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2014, 58, 7451–7461 CrossRef . For C. neoformans, see:; (c) M. J. Donlin, A. Zunica, A. Lipnicky, A. K. Garimallaprabhakaran, A. J. Berkowitz, A. Grigoryan, M. J. Meyers, J. E. Tavis and J. R. P. Murelli, Troponoids can inhibit growth of the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2017, 61, e02574–16 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. Didierjean, C. Isel, F. Querre, J. F. Mouscadet, A. M. Aubertin, J. Y. Valnot, S. R. Piettre and R. Marquet, Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase, RNase H, and integrase activities by hydroxytropolones, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2005, 49, 4884–4894 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. Chung, D. M. Himmel, J. K. Jiang, K. Wojtak, J. D. Bauman, J. W. Rausch, J. A. Wilson, J. A. Beutler, C. J. Thomas, E. Arnold and S. F. J. Le Grice, Synthesis, activity, and structural analysis of novel α-hydroxytropolone inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 4462–4473 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For lead reference, see: C. Meck, N. Mohd and R. P. Murelli, An oxidopyrylium cyclization/ring-opening route to polysubstituted α-hydroxytropolones, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 5988–5991 CrossRef CAS.
- For a representative example, see: D. R. Hirsch, D. V. Schiavone, A. J. Berkowitz, L. A. Morrison, T. Masaoka, J. A. Wilson, E. Lomonosova, H. Zhao, B. S. Patel, S. H. Dalta, S. J. Majidi, R. K. Pal, E. Gallicchio, L. Tang, J. E. Tavis, S. F. J. Le Grice, J. A. Beutler and R. P. Murelli, Synthesis and biological assessment of 3,7-dihydroxytropolones, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2018, 16, 62–69 RSC.
- S. R. Piettre, C. Andre, M. C. Chanal, J. B. Ducep, B. Lesur, F. Piriou, P. Raboisson, J. M. Rondeau, C. Schelcher, P. Zimmermann and A. J. Ganzhorn, Monoaryl- and bisaryldihydroxytropolones as potent inhibitors of inositol monophosphatase, J. Med. Chem., 1997, 40, 4208–4221 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kubo and A. Mori, “Synthesis and mercurophilic properties of acyclic and thiolariat ethers having tropone pendant”, Heterocycles, 2001, 54, 351–358 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Takeshita; M. Akira; and K. Tomoyuka, “An improved synthesis of 2,7-dihydroxytropone (3-hydroxytropolone)” synthesis, 1986, pp. 578–579 Search PubMed.
- K. Hassenberg, J. Pickardt and R. Steudel, Oxidation products of 1,2,3-trithia [3] ferrocenophane: structures of the corresponding sulfoxide and sulfone, Organometallics, 2000, 19, 5244–5246 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) G. Lu, E. Lomonosova, X. Cheng, E. A. Moran, M. K. Meyers, S. F. J. Le Grice, C. J. Thomas, J.-K. Jiang, C. Meck, D. R. Hirsch, M. P. D'Erasemo, D. M. Suyabatmaz, R. P. Murelli and J. E. Tavis, Hydroxylated tropolones inhibit hepatitis B virus replication by blocking the viral ribonuclease H activity, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2015, 59, 1070–1079 CrossRef; (b) E. Lomonosova, J. Daw, A. K. Garimallaprabhakaran, N. B. Agyemang, Y. Ashani, R. P. Murelli and J. E. Tavis, Efficacy and cytotoxicity in cell culture of novel α-hydroxytropolone inhibitors of hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H, Antiviral Res., 2017, 144, 164–172 CrossRef CAS.
- P. J. Ireland, J. E. Tavis, M. P. D'Erasmo, D. R. Hirsch, R. P. Murelli, M. M. Cadiz, B. S. Patel, A. K. Gupta, T. C Edwards, M. Korom, E. A. Moran and L. A. Morrison, Synthetic α-hydroxytropolones inhibit replication of wild-type and acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex viruses, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2016, 60, 2140–2149 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Guo, D. Jiang, T. Zhao, A. Cuconati, T. M. Block and J.-T. Guo, Characterization of the intracellular deproteinized relaxed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus: an intermediate of covalently closed circular DNA formation, J. Virol., 2007, 81, 12472–12484 CrossRef CAS.
- R. J. Whitley, Herpes simplex viruses, in Fields Virology, D. Knipe and P. Howley, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, 4th edn, 2001, vol. 2, pp. 2461–2509 Search PubMed.
- A. V. Farooq and D. Shukla, Herpes simplex epithelial and stromal keratitis: an epidemiologic update, Surv. Ophthalmol., 2012, 57, 448–462 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) R. J. Whitley, Herpes simplex encephalitis: adolescents and adults, Antiviral Res., 2006, 71, 141–148 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. Johnston, M. Saracino, S. Kuntz, A. Magaret, S. Selke, M. L. Huang, J. T. Schiffer, D. M. Koelle, L. Corey and A. Wald, Standard-dose and high-dose daily antiviral therapy for short episodes of genetal HSV-2 reactivation: three randomized, open-label, cross-over trails, Lancet, 2012, 379, 641–647 CrossRef CAS; (c) R. Duan, R. D. de Vries, A. D. Osterhaus, L. Remeijer and G. M. Verjans, Acyclovir-resistant corneal HSV-1 isolates from patients with herpetic keratitis, J. Infect. Dis., 2008, 198, 659–663 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Masaoka, H. Zhao, D. R. Hirsch, M. P. D'Erasmo, C. Meck, B. Varnado, A. Gupta, M. J. Meyers, J. D. Baines, J. A. Beutler, R. P. Murelli, L. Tang and S. F. J. Le Grice, Characterization the C-terminal nuclease domain of herpes simplex virus pUL15 as a target of nucleotidyltransferase inhibitors, Biochemistry, 2016, 55, 809–819 CrossRef CAS.
- L. M. Grady, R. Szczepaniak, R. P. Murelli, T. Masaoka, S. F. J. Le Grice, D. L. Wright and S. K. Weller, The exonuclease activity of HSV-1 UL12 is required for the production of viral DNA that can be packaged to produce infectious virus, J. Virol., 2017, 91, e01380–17 CrossRef CAS.
- J. T. Miller, H. Zhao, T. Masaoka, B. Varnado, E. M. Cornejo Castro, V. A. Marshall, K. Kouhestani, A. Y. Lynn, K. E. Aron, A. Xia, J. A. Beutler, D. R. Hirsch, L. Tang, D. Whitby, R. P. Murelli and S. F. J. Le Grice, Sensitivity of the C-terminal nuclease domain of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF29 to two classes of active site ligands, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2018, 62, e00233-18 CrossRef.
- S. D. Dehghanpir, C. H. Birkenheuer, K. Yang, R. P. Murelli, L. A. Morrison, S. F. J. Le Grice and J. D. Baines, Broad anti-herpesviral activity of α-hydroxtropolones, Vet. Microbiol., 2018, 214, 125–131 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Berkowitz, A. D. Franson, A. Gazquez Cassals, K. A. Donald, A. J. Yu, A. K. Garimallaprabhakaran, L. A. Morrison and R. P. Murelli, Importance of lipophilicity for potent anti-herpes simplex virus-1 activity of α-hydroxytropolones, MedChemComm, 2019, 10, 1173–1176 RSC.
- R. Rajasingham, R. M. Smith, B. J. Park, J. N. Jarvis, N. P. Govender, T. M. Chiller, D. W. Denning, A. Loyse and D. R. Boulware, “Global burden of disease of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: an updated analysis”, Lancet Infect. Dis., 2017, 17, 873–881 CrossRef.
- D. Neofytos, J. A. Fishman, D. Horn, E. Anaissie, C. H. Chang, A. Olyaei, M. Pfaller, W. J. Steinbach, K. M. Webster and K. A. Marr, Epidemiology and outcome of invasive fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients” Transpl, Lancet Infect. Dis., 2010, 12, 220–229 CAS.
- W. H. O., Hepatitis B: World Health Organization Fact Sheet. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b accessed June 4, 2019 Search PubMed.
- (a) B. Sebastien, B. Leda, E. Maryam and R. F. Schinazi, “Towards elimination of hepatitis B virus using novel drugs, approaches, and combined modalities”, Clin. Liver Dis., 2016, 20, 737–749 CrossRef; (b) A. P. Revill, F. V. Chisari, J. M. Block, M. Dandri, A. J. Gehring, H. Guo, J. Hu, A. Kramvis, P. Lampertico, H. L. A. Janssen, M. Levrero, W. Li, T. J. Liang, S. G. Lim, F. Lu, M. C. Penicaud, J. E. Tavis, R. Thimme, Members of the I. C. E.-H. B. V. Working Groups, I. C. E.-H. B. V. Stakeholders Groups Chairs, I. C. E.-H. B. V. Senior Advisors and F. Zoulim, A global scientific strategy to cure hepatitis B, The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2019, 4, 545–558 Search PubMed.
- S. Feng, L. Gao, X. Han, T. Hu, Y. Hu, H. Liu, A. W. Thomas, Z. Yan, S. Yang, J. A. T. Young, H. Yun, W. Zhu and H. C. Shen, Discovery of small molecule therapeutics for treatment of chronic HBV infection, ACS Infect. Dis., 2018, 4, 257–277 CrossRef CAS.
- J. S. Emery and J. J. Feld, Treatment of hepatitis B virus with combination therapy now and in the future, Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol., 2017, 31, 347–355 CrossRef CAS.
- K. R. Long, E. Lomonosova, W. Li, N. L. Ponzar, J. A. Villa, E. Touchette, S. Rapp, R. M. Liley, R. P. Murelli, A. Grigoryan, R. M. Buller, L. Wilson, J. Bial, J. E. Sagartz and J. E. Tavis, Efficacy of hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H inhibitors, a new class of replication antagonists, in FRG human liver chimeric mice, Antiviral Res., 2018, 149, 41–47 CrossRef CAS.
- J. E. Tavis, G. Zoidis, M. J. Meyers and R. P. Murelli, Chemical approaches to inhibiting the hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H, ACS Infect. Dis., 2019, 5, 655–658 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Stasiak, A. Grigoryan and R. P. Murelli, Spectrophotometric determination of α-hydroxytropolone pKa values, Tetrahedron Lett., 2019, 60, 1643–1645 CrossRef CAS.
- T. C. Edwards, E. Lomonosova, J. A. Patel, Q. Li, J. A. Villa, A. K. Gupta, L. A. Morrison, F. Bailly, P. Cotelle, E. Giannakopoulou, G. Zoidis and J. E. Tavis, Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by N-hydroxyisoquinolinediones and related polyoxygenated heterocycles, Antiviral Res., 2017, 143, 205–217 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06383h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |