Correlation between polymer architecture and polyion complex micelle stability with proteins in spheroid cancer models as seen by light-sheet microscopy†
Abstract
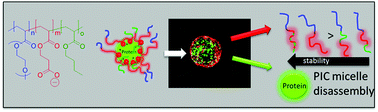
Polyion complex (PIC) micelles are frequently used as a means to deliver biologics such as proteins. While it is known that the polymer structure can affect the stability of these micelles, few studies have investigated their stability in biological settings. In this paper, we have prepared a library of poly[poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether acrylate]-block-poly(2-carboxyethyl acrylate)s (PPEGMEA-b-PCEA) and poly[poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether acrylate]-block-poly(acrylic acid)s (PPEGMEA-b-PAA), each with varying chain length of the charged polymer block. In addition terpolymers were prepared that included hydrophobic n-butyl acrylate (BA) units randomly incorporated along the charged block and as triblock terpolymers (PPEGMEA-b-(PCEA-co-PBA), PPEGMEA-b-PCEA-b-PBA or PPEGMEA-b-PBA-b-PCEA). These polymers were condensed with lysozyme to generate PIC micelles of various compositions. While stable in the intracellular space, the diblock PIC micelles readily disassembled inside the cells of spheroid cancer models as evidenced by light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) and Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) studies. Terpolymer PIC micelles were more resistant to disassembly, but only when the hydrophobic BA groups were randomly distributed within the pCEA blocks and not when incorporated as a separate block. These results show that simple PIC micelles will rapidly deliver biological cargo after cell internalization and their stability can be tuned by the introduction of hydrophobic units within the charged block.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...