Formation of i-motifs from acyclic (l)-threoninol nucleic acids†
Abstract
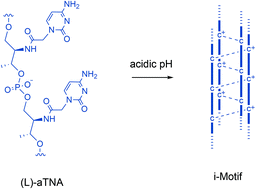
Acyclic (L)-threoninol nucleic acids ((L)-aTNA) containing poly-cytosines are prepared and investigated at various pH values, revealing the formation of a highly stable structure at lower pH that have the characteristics of an i-motif. Depending on the sequence, the aTNA forms inter-, bi- and intra-molecular i-motif structures. Pyrene was conjugated to aTNA sequences and both monomeric and excimer fluorescence were efficiently quenched by the i-motif structures and thus demonstrated that the aTNA i-motif can serve as a pH switch.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...