Surfacing amorphous Ni–B nanoflakes on NiCo2O4 nanospheres as multifunctional bridges for promoting lithium storage behaviors†
Abstract
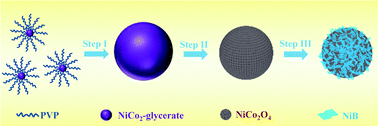
Transition metal oxides (TMOs) have gained enormous research interests as negative materials of next generation lithium-ion batteries due to their higher energy density, lower cost, and better eco-friendliness. However, they are prone to low electronic conductivities and dramatic volume change during charge/discharge and there is also a great challenge in realizing TMO electrodes with satisfactory LIB performances. In this study, for the first time, amorphous nickel–boride (Ni–B) was introduced into porous NiCo2O4 nanospheres by an in situ solution growth route to overcome the existing issues. The coated Ni–B component could not only function as anchors for NiCo2O4 nanospheres to suppress the severe volume expansion but could also act as effective electron-conducting bridges to promote fast electron/charge transfer. Furthermore, the existence of abundant mesopores centered at ∼6.5 nm in this composite could effectively suppress the severe volume variations in the lithiation/delithiation process. As expected, the NiCo2O4@Ni–B composites delivered a high reversible capacity of 1221 mA h g−1 at 0.2 A g−1 and 865 mA h g−1 at 0.5 A g−1 over 500 cycles; more impressively, at the high rate of 5 A g−1, a capacity of 648 mA h g−1 could be also obtained, showing its good rate capability. As a result, these results demonstrated an effective and facile way to design conversion-type negative electrode materials with superior lithium storage properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...