A protein nanocontainer targeting epithelial cancers: rational engineering, biochemical characterization, drug loading and cell delivery†
Abstract
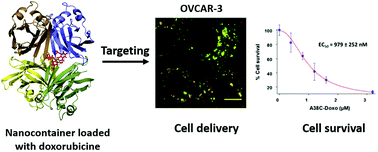
The development of drug delivery and imaging tools is a major challenge in human health, in particular in cancer pathologies. This work describes the optimization of a protein nanocontainer, belonging to the lectin protein family, for its use in epithelial cancer diagnosis and treatment. Indeed, it specifically targets a glycosidic marker, the T antigen, which is known to be characteristic of epithelial cancers. Its quaternary structure reveals a large hydrated inner cavity able to transport small therapeutic molecules. Optimization of the nanocontainer by site directed mutagenesis allowed controlling loading and release of confined drugs. Doxorubicin confinement was followed, both theoretically and experimentally, and provided a proof of concept for the use of this nanocontainer as a vectorization system. In OVCAR-3 cells, a human ovarian adenocarcinoma cell line that expresses the T antigen, the drug was observed to be delivered inside late endosomes/lysosomes. These results show that this new type of vectorization and imaging device opens new exciting perspectives in nano-theranostic approaches.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...