A mechanically robust silver nanowire–polydimethylsiloxane electrode based on facile transfer printing techniques for wearable displays†
Abstract
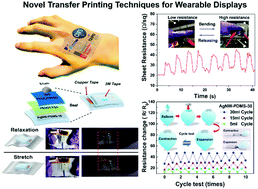
Silver nanowire (AgNW) networks have attracted considerable attention as transparent electrodes for emerging flexible optoelectronics. However, the transference of such networks onto diverse arbitrary substrates with high conductivity remains a challenge because of the possibility of detaching and sliding occurring at the interface. Therefore, we developed a water-assisted transfer printing method for the fabrication and transfer of an AgNW–polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) electrode. This innovative approach exhibits a robust ability for thin film transfer onto arbitrary substrates and has highly controlled and nondestructive characteristics. The obtained electrodes exhibited a high ratio of DC conductivity to optical conductivity of 200, a low sheet resistance of 9 Ω sq−1 at 82%, tensile strain (0% to 50%), and flexibility (bending radius of less than 2 mm) without significant loss of conductivity compared with devices fabricated through conventional methods. Furthermore, we demonstrated a novel textile-based flexible light-emitting electrochemical cell (PLEC) based on the stretchable AgNW–PDMS electrode and buckling concept, thereby realizing highly stretchable PLECs with excellent performance and mechanical robustness. The luminance intensity of the strained device was optimized to 58 cd m−2 at 7 V under 10% linear strain without damaging the electroluminescence properties. Notably, this effective and practical transfer method provides a way to develop electronic nanowire devices with unique configurations and high performances.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...