An electrochemical immunosensor based on a combined amplification strategy with the GO–CS/CeO2–CS nanocomposite for the detection of aflatoxin M1
Abstract
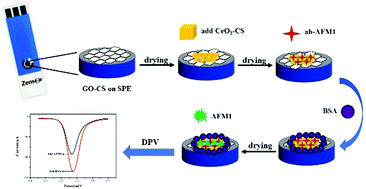
In this paper, a sensitive electrochemical immunosensor modified with graphene oxide–chitosan (GO–CS) and cerium oxide–chitosan (CeO2–CS) using screen-printed electrodes (SPEs) was developed for the determination of aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) in milk. Compared with other electrodes, SPEs are easy for quick detection and no polishing steps are required. Graphene oxide (GO) has strong electrical conductivity and a large specific surface area, which can accelerate the transfer of electrons and fix more anti-AFM1 antibodies (ab-AFM1) on SPEs. Compared with GO, cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles have a smaller diameter, and CeO2 can be uniformly attached to the surface of the GO. Simultaneously, CeO2 has good redox properties and can further accelerate the transfer of electrons, thereby further amplifying the electrochemical signal of the sensor. Chitosan (CS) has strong complexation ability, which can uniformly disperse GO and CeO2. Herein, GO–CS and CeO2–CS gradually modified SPEs to improve their electrochemical response and immobilize more antibodies. The properties of the AFM1 immunosensor were studied via differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and cyclic voltammetry (CV). Under the optimal conditions, the immunosensor showed great reproducibility and high stability with a detection limit of 0.009 μg L−1. In addition, the immunosensor was successfully utilized for the determination of AFM1 in milk. This immunosensing principle will have broad prospects for the analysis of toxins in food, ensuring the safety of milk and dairy products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...