Identification and structural characterization of the stress degradation products of omeprazole using Q-TOF-LC-ESI-MS/MS and NMR experiments: evaluation of the toxicity of the degradation products†
Abstract
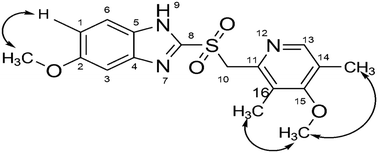
Omeprazole (OMP), a prototype proton pump inhibitor used for the treatment of peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), was subjected to forced degradation studies as per ICH guidelines Q1A (R2). The drug undergoes degradation under acid, base, neutral hydrolysis and oxidative degradation conditions and forms a total of sixteen degradation products, which were characterized by LC-MS/MS experiments and accurate mass measurements. Oxidative degradation products (OMP-15 and OMP-16) were synthesized and confirmed by various NMR experiments. The cytotoxic effects of OMP-15 and OMP-16 were tested on normal human cells HEK 293 and NIH3T3 by MTT assay. Based on the cytotoxicity results, compared to the standard OMP, both OMP-15 and OMP-16 were found to have relatively weaker toxic effects towards normal cells. Further, the in silico toxicity of OMP and its degradation products (OMP-1 to OMP-16) was assessed by the ProTox-II prediction tool. OMP and OMP-8 are predicted to have carcinogenicity, OMP-7 to have hepatotoxicity and OMP-2, OMP-3, OMP-9, OMP-11, OMP-14 and OMP-16 to have immune system toxicity with a high confidence score. The drug, OMP-1, OMP-6, OMP-7, OMP-8, OMP-13 and OMP-15 are predicted to combine with the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) with a high probability score. Additionally, two different targets, amine oxidase A and prostaglandin G/H synthase 1, are predicted as toxicity targets for OMP, OMP-1, OMP-6, OMP-8, OMP-13, OMP-15 and OMP-16 with probable binding.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...