Structure-directing effect of single crystal graphene film on polymer carbonization and graphitization†
Abstract
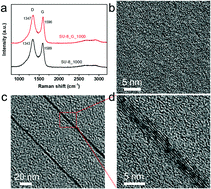
We report the effect of single crystal graphene on carbonization and graphitization of thin film polymers. Electron microscopy reveals that at the early stages of carbonization, graphene induces the carbon atoms in its near vicinity to form oriented layers parallel to the graphene layer. At elevated temperatures, these layers develop further to form extended graphitic (002) planes parallel to the graphene surface. For the samples which were heat treated and graphitized, grazing incidence X-ray scattering reveals that graphene narrows the distribution of graphite grain orientations. Based on these results, we propose that graphene can act as a structure directing agent in both the carbonization and graphitization of polymer thin films, and may provide an approach to realize single crystal graphite films, perhaps in combination with established techniques such as stress recrystallization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...