Amide linked redox-active naphthoquinones for the treatment of mitochondrial dysfunction†
Abstract
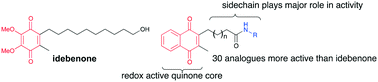
Naphthoquinones have been investigated as potential therapeutic molecules for neurodegenerative disorders, which is largely based on their anti-oxidative potential. However, a theoretical framework for the pleiotropic protective effects of naphthoquinone derivatives is largely missing. We synthesized a library of novel short chain 2,3-disubstituted naphthoquinone derivatives and measured their redox characteristics to identify a potential connection with their biological activity. Using two cell lines with different reducing potential, the compounds were tested for their inherent toxicity, acute rescue of ATP levels and cytoprotective activity. For the first time, a structure–activity-relationship for naphthoquinones has been established. Our results clearly demonstrate that it is the group on the alkyl side chain and not solely the redox characteristics of the naphthoquinone unit or lipophilicity that determines the extent of cytoprotection by individual compounds. From this, we developed a number of amide containing naphthoquinones with superior activity in ATP rescue and cell viability models compared to the clinically used benzoquinone idebenone.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...