An ultra-rapid acoustic micromixer for synthesis of organic nanoparticles†
Abstract
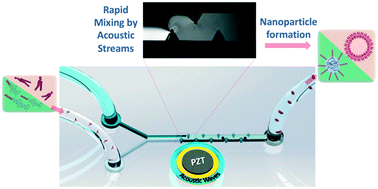
Mixing is a crucial step in many chemical analyses and synthesis processes, particularly in nanoparticle formation, where it determines the nucleation rate, homogeneity, and physicochemical characteristics of the products. In this study, we propose an energy-efficient acoustic platform based on boundary-driven acoustic streaming, which provides the rapid mixing required to control nanoprecipitation. The device encompasses oscillatory bubbles and sharp edges in the microchannel to transform the acoustic energy into vigorous vortical fluid motions. The combination of bubbles and sharp edges at their immediate proximity induced substantially stronger acoustic microstreams than the simple superposition of their effects. The device could effectively homogenize DI water and fluorescein within a mixing length of 25.2 μm up to a flow rate of 116 μL min−1 at a driving voltage of 40 Vpp, corresponding to a mixing time of 0.8 ms. This rapid mixing was employed to mitigate some complexities in nanoparticle synthesis, namely controlling nanoprecipitation and size, batch to batch variation, synthesis throughput, and clogging. Both polymeric nanoparticles and liposomes were synthesized in this platform and showed a smaller effective size and narrower size distribution in comparison to those obtained by a hydrodynamic flow focusing method. Through changing the mixing time, the effective size of the nanoparticles could be fine-tuned for both polymeric nanoparticles and liposomes. The rapid mixing and strong vortices prevent aggregation of nanoparticles, leading to a substantially higher throughput of liposomes in comparison with that by the hydrodynamic flow focusing method. The straightforward fabrication process of the system coupled with low power consumption, high-controllability, and rapid mixing time renders this mixer a practical platform for a myriad of nano and biotechnological applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...