Switching on palladium catalyst electrochemical removal from a palladium acetate–acetonitrile system via trace water addition†
Abstract
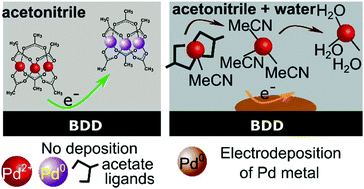
Palladium acetate (Pd-acetate) is a common catalyst used in a wide array of organic synthetic reactions in non-aqueous solvents. Due to its high cost and associated toxicity/contamination issues in reaction mixtures, Pd removal and recovery is essential. Here we explore the use of electrodeposition as a means to remove Pd from an acetonitrile (MeCN) based Suzuki cross coupling reaction solution, by plating metallic Pd onto the surface of an electrode (boron doped diamond). We show the importance of adding tolerable volumes of water to the reaction mixture in order to facilitate the electrodeposition process. In MeCN, strong coordination bonds exist between the Pd cation and acetate groups and electrodeposition is not possible. By adding water in controlled quantities we show using spectroscopic, electrochemical and microscopic techniques that acetate ligands are released from Pd co-ordination and first replaced by MeCN molecules, enabling electrodeposition. As the water content increases, the MeCN co-ordinating molecules are replaced by water, due to the favourable water–MeCN interactions overcoming those of Pd cation–MeCN, also promoting electrodeposition. We show that sufficient perturbation of the Pd-acetate structure to enable electrodeposition is possible in MeCN solutions containing as little as 5% water (v/v). We demonstrate 99.4% removal of Pd, as metallic Pd plated onto the electrode surface, from a Suzuki reaction solution, using electrochemical methods.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Green Chemistry Hot Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...