A lignin-containing cellulose hydrogel for lignin fractionation†
Abstract
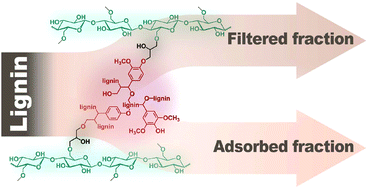
With the implementation of the strategy of sustainable development, solving resource problems is key to the development of the chemical industry. As the most abundant renewable resource of aromatic building blocks in nature, lignin has great potential as a starting material for functional materials and energy conversion. However, owing to lignin's heterogeneity, the target of scaled-up application of lignin resources is far from being realized. To address this challenge, in this work, a novel hydrogel-assisted fractionation approach using lignin-containing cellulose (Cell-AL) hydrogel was developed to fractionate lignin to produce uniform lignins. Cell-AL hydrogels were synthesized by introducing alkaline lignin as the functional cross-linker to simultaneously achieve mechanical enhancement of the hydrogel and specific adsorption or filtration of lignin molecules. After fractionating by Cell-AL, the molecular weights of the adsorbed and filtered lignin fractions showed a decrease and increase, respectively. The polydispersity index of all the lignin fractions was obviously reduced. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis revealed that the lignin fractions exhibited higher contents of aliphatic structures and lower contents of phenolic structures without cleaving linkages. In addition, the ratio of lignin functional cross-linker had a marked influence on the hydrogel properties and obtained structures of lignin fractions. This lignin-containing hydrogel-assisted technology offers a promising approach to combine two aspects of biorefinery for lignin fractionation and lignin materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...