Electrochemical synthesis of enaminones via a decarboxylative coupling reaction†
Abstract
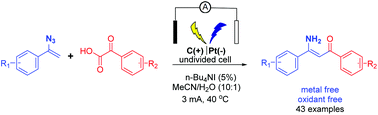
An environmentally benign and efficient electrochemical synthesis of enaminones via a decarboxylative coupling reaction of α-keto acids using n-Bu4NI as a redox catalyst and electrolyte under constant current electrolysis in an undivided cell is reported. A broad vinyl azide substrate scope and high functional group tolerance are observed. A gram-scale reaction further demonstrates the practicability of the protocol. The results of cyclic voltammetry and control experiments indicate that I2 is likely the active species to initiate the oxidative decarboxylation via an acyl hypoiodite intermediate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...