A faster and simpler UPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of trimethylamine N-oxide, trimethylamine and dimethylamine in different types of biological samples
Abstract
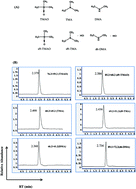
Gut microbiota-dependent metabolites trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), trimethylamine (TMA) and dimethylamine (DMA) from dietary methylamines have recently gained much attention due to their high association with chronic kidney disease risk. Hence a simpler and faster performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method was developed and validated. The quantitative analysis was achieved within 6 min by using Agilent 6460C UPLC-MS/MS with 10% methyl alcohol isocratic elution and was more simple, convenient and rapid than that of previously reported methods. Furthermore, method verification results showed that the method correlation coefficient was 0.99978293, 0.99997514 and 0.98784721, and the detection limit was 0.121, 8.063 and 0.797 μg L−1, and the precision of the retention time and peak area of analytes was less than 0.331 and 3.280, respectively. The method was applied to simultaneously determine TMAO, TMA and DMA in the urine and serum from mice treated with normal, high L-carnitine, or high choline diet. Quantitative recoveries of TMAO, TMA and DMA were in the range of 94.2%–101.0%, and the RSD values were lower than 5.17%. The proposed UPLC-MS/MS-based assay should be of value for further evaluating TMAO as a risk marker and for examining the effect of dietary factors on TMAO metabolism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...