Photocatalytic degradation of polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) on metal doped TiO2 nanocomposites in aqueous environments: mechanisms and solution effects†
Abstract
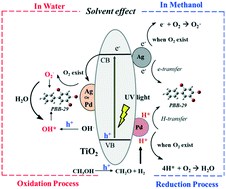
This study investigated the photocatalytic degradation of polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) by metal doped titanium dioxide (M/TiO2). The results indicate that Pd and Ag can greatly enhance the reactivity of TiO2 to 2,4,5-tribromobiphenyl (PBB-29), but its debromination pathways by Ag/TiO2 and Pd/TiO2 are not the same. PBB-29 can be rapidly degraded by Pd/TiO2 without a light source by purging H2 into the system, and the debromination pathways of PBB-29 in this system (i.e., Pd/TiO2–H2) are exactly the same as those in Pd/TiO2-UV systems, suggesting that Pd can utilize the generated H2 to debrominate PBBs through an H-transfer process. When the system solvent shifted from methanol to water, the degradation mechanism of PBBs changed from reductive debromination to an oxidation process. The results of PBB kinetics and the electron paramagnetic resonance spectra supported this conclusion. In addition, when the system solvent is methanol, O2 can greatly inhibit the reactivity of Pd/TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 by capturing the active H atoms and electrons, respectively. When the solvent was changed to water, O2 exerted a negligible effect on the degradation of PBBs by these two materials, because the generation of hydroxyl radicals was not reduced.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...