Discovery of high in vitro and in vivo antitumor activities of organometallic ruthenium(ii)–arene complexes with 5,7-dihalogenated-2-methyl-8-quinolinol†
Abstract
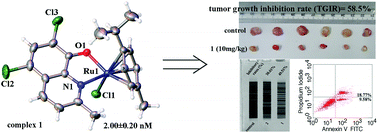
This paper reports the synthesis, structure characterization, and anticancer properties of 13 organometallic Ru(II)–arene complexes: [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl-(L1)] (1), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl-(L2)] (2), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl-(L3)] (3), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl-(L4)] (4), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl-(L5)] (5), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)I-(L1)] (6), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)I-(L2)] (7), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)I-(L3)] (8), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)I-(L4)] (9), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)I-(L5)] (10), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)I-(L6)] (11), [Ru(η6-p-cymene)I-(L7)] (12), and [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl-(L8)] (13) respectively containing deprotonated 5,7-dichloro-2-methyl-8-quinolinol (H-L1), 5,7-dibromo-2-methyl-8-quinolinol (H-L2), 5-chloro-7-iodo-8-hydroxy-quinoline (H-L3), 5,7-dibromo-8-quinolinol (H-L4), 5,7-diiodo-8-hydroxyquinoline (H-L5), 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinoline (H-L6), 2,8-quinolinediol (H-L7), or 6,7-dichloro-5,8-quinolinedione (H-L8). MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay showed that 13 organometallic Ru(II)–arene complexes 1–13 are more selective for HeLa cells than normal HL-7702 cells. In addition, 1, 2, 5, and 6, which contain the active ligands H-L1 and H-L2, showed remarkable cell cytotoxicity, giving the respective IC50 values of 2.00 ± 0.20 nM, 0.89 ± 0.62 μM, 25.00 ± 0.30 nM, and 2.18 ± 0.35 μM on HeLa cancer cells. These values indicated higher activity than 6,7-dichloro-5,8-quinolinedione and other 8-hydroxyquinoline derivative Ru(II)–arene complexes. Interestingly, all these Ru(II)–arene complexes 1–13 were significantly less toxic to human hepatic (HL-7702) cells. Moreover, 1- and 2-induced HeLa cell apoptosis was mediated by the inhibition of telomerase activity and dysfunction of mitochondria, and resulted in DNA damage and increased anti-migration activity on HeLa cells. The organometallic Ru(II)–arene complex 1 exhibited evident priority to the antitumor activity compared to 2, which should be highly associated with the key roles of the 5,7-dichloro substituted groups in the L1 ligand of organometallic Ru(II)–arene complexes 1. Remarkably, 1 showed higher inhibitory activity against the xenograft tumor growth of human cervical cells (HeLa) in vivo (tumor growth inhibition rate (TGIR) = 58.5%) than cisplatin. This study was the first to show that the 5,7-dihalogenated-2-methyl-8-quinolinol organometallic Ru(II)–arene complexes 1 and 2 are novel Ru(II) anticancer drug candidates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...