Tuning the N-bonded cerium(iii) fraction/g-C3N4 interface in hollow structures using an in situ reduction treatment for superior photochemical hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
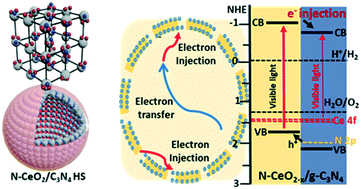
The synthesis of inorganic/organic interfaces in spherical hollow structures (HS) is a promising but challenging task. Herein, we innovatively utilized porous CeO2-HS as a scaffold to incorporate cyanamide molecules, which upon one-step in situ reducing treatment, yielded nitrogen-bonded CeO2−x/g-C3N4-HS. The electron microscope and spectroscopic analysis validated two functions of cyanamide: i) it generates an in situ reducing atmosphere (CO, N2, NOx) to tune the cerium oxide vacancy population, and ii) it acts as a N and g-C3N4 precursor. Meanwhile, the unique HS geometry promotes cerium oxide reduction at low temperature due to the following: i) the high surface area of CeO2-HS provides a larger area for CeO2/CO interaction; ii) adequate pore volume enhances the cerium oxide reduction kinetics; and, iii) the CeO2 nanoparticles increase the ceria surface defect population by obeying the ceria oxygen vacancy transport model. Remarkably, the N-CeO2−x/g-C3N4-HS photocatalyst hydrogen evolution rate is 43.32 μmol g−1 h−1 under visible light (λ ≥ 420 nm), which is 3.8 times higher than pristine g-C3N4 (11.4 μmol g−1 h−1) due to: a) enhancement of the material's light-harvesting ability by HS, b) formation of controlled optically active Ce3+ sites, and c) intimate inorganic/organic interfaces, which boosted the minority carriers' separation efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...